What is an ISO audit? Preparation and tips
How does an ISO audit work, and how can your team best prepare for one? This article takes a look at all the main concerns, as well as how skills management can come in handy.

The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) is an independent, international organization that develops and publishes standards for a wide range of industries and sectors.
Becoming officially certified in these standards, however, requires periodic audits to ensure that an organization is compliant.
In this article, we’ll take a look at ISO as an organization, the benefits its standards bring to businesses, the various types of ISO audits, tips for preparation, and more.
What is ISO?Copied
ISO standards are designed to ensure the quality, safety, efficiency, interoperability, and consistency of products, services, and systems. They cover a broad range of topics, and are in all probability highly familiar to those working within certain industries.
They cover, but are not limited to, the following areas:
- Quality management. ISO 9001 is a well-known standard for quality management systems used by organizations to demonstrate their commitment to quality and customer satisfaction.
- Environmental management. ISO 14001 provides guidelines for establishing an environmental management system to help organizations minimize their environmental impact.
- Information security. ISO 27001 sets out best practices for information security management systems to protect sensitive data.
- Occupational health and safety. ISO 45001 offers a framework for occupational health and safety management systems to promote workplace safety.
- Food safety. ISO 22000 outlines requirements for food safety management systems, ensuring the safety of food products throughout the supply chain.
- Energy management. ISO 50001 assists organizations in managing and improving energy performance and reducing energy consumption.
The benefits of ISO certificationCopied
While ISO certifications are typically not mandatory for organizations, they do act as signals to customers or clients that a business is committed to excellence in various areas of business operations. Unsurprisingly, this often has a positive effect on ISO-certified businesses [1].
In its white paper, “Economic Benefits of Standards,” the ISO reports that business that are compliant with ISO standards see:
- Streamlined internal processes, resulting in annual sales revenue increases of up to 5%.
- Innovations to existing processes that enable businesses to “expand their suppliers’ network or introduce and manage new product lines effectively.
- Improved strategies for creating new products or entering new markets, which in some cases results in annual revenue increases of up to 33%.
Additionally, the ISO outlines several of the more general benefits that compliance with and certification in ISO standards bring to businesses. They include [2]:
Improved customer confidence
ISO compliance assures customers that your products or services meet stringent safety and quality standards. This builds trust and confidence in your brand, leading to increased customer loyalty and positive word-of-mouth recommendations.
Ability to more easily meet regulation requirements
ISO standards provide a structured framework for regulatory compliance. By aligning with these standards, you can efficiently adhere to legal requirements, reducing the risk of fines or penalties. This proactive approach often proves more cost-effective than addressing non-compliance issues after the fact.
Reduced operational costs
ISO compliance encourages process optimization and waste reduction, resulting in cost savings. By consistently reviewing and improving operations, you can identify inefficiencies, cut unnecessary expenses, and enhance overall profitability.
Increased global market access
ISO certification is internationally recognized and respected. Achieving ISO compliance opens doors to global markets by demonstrating your commitment to quality and safety. This broader market access can lead to increased sales and business growth on a global scale.
Compliance and certification with ISO standards, however, requires businesses to undergo or conduct an ISO audit. In the next sections, we’ll examine the definition of an ISO audit, its various types, and offer a few tips for preparing for them.
What is an ISO audit?Copied
An ISO audit is a systematic examination of an organization’s processes, systems, and compliance with ISO standards. It ensures adherence to established best practices, quality, and regulatory requirements.
Who conducts an ISO audit?Copied
The ISO itself does not conduct audits or act as a certification body, instead focusing solely on developing its international standards. Should an organization seek certification, they must use an accredited certification body, which may also conduct an ISO audit.
The specific entity conducting the ISO audit depends on the purpose of the audit, the standards being audited against, and the organization’s specific requirements. Here are a few common categories of ISO audits.
Internal audits
Internal ISO audits (also known as first-party audits) are conducted by internal auditors or audit teams within an organization.
These auditors are typically employees trained in ISO standards and audit procedures. Internal audits help organizations assess their own compliance and identify areas for improvement.
Supplier audits
Supplier audits (or second-party audits) evaluate external vendors’ compliance quality, safety, and compliance standards. In a supplier audit, organizations assess their suppliers’ processes, documentation, and performance to ensure products or services meet ISO standards. This helps ensure both companies – the supplier and the auditing organization – remain compliant, as they both rely on one another to ensure they adhere to the standards.
For example, if a medical device manufacturer audits its component supplier and finds non-compliance, the manufacturer is non-compliant by proxy. In such a situation, corrective actions can be taken to rectify issues, maintaining product quality and regulatory compliance throughout the supply chain.
Third-party audits
Third-party audits, or external audit, are conducted by external auditors who are not directly affiliated with the organization being audited. They provide an unbiased assessment and are commonly used for audits in which a higher level of objectivity is required.
Examples of audits that would require a third party to conduct them include regulatory audits, which ensure compliance with industry regulations, or a final certification audit from an accredited ISO certification body.
How to prepare for an ISO auditCopied
In an article on obtaining ISO certification, Forbes recommends splitting your preparation for an ISO audit into three categories [3]:
- Organizational
- Legal
- Technical
By doing so, your teams can better organize and focus on the myriad standards to which your organization must comply. It’s worth noting here that, depending on the ISO standard being audited, the importance of certain categories may be more or less important.
For instance, a standard that emphasizes the importance of having a well-defined organizational structure, documented processes, and a strong commitment to customer satisfaction or environmental responsibility will mean the “organizational” category is more important.
In contrast, a standard that places heavy emphasis on technical controls, information security policies, risk assessments, and safeguarding sensitive data will see organizations preparing more in the “technical” category.
This means that tailoring preparations based on the standard’s emphasis is essential for successful certification. With that in mind, let’s take a look at each of three categories that can help you prepare for an ISO audit.
Organizational
The organizational category encompasses an organization’s overall structure, policies, and processes
Here, businesses need to demonstrate that they have established:
- Clear objectives
- Documented procedures
- And a robust management system that aligns with the relevant ISO standard
The organizational category also includes aspects such as leadership commitment, resource allocation, communication, and continuous improvement.
Legal
Compliance with legal and regulatory requirements is crucial for ISO certification. Organizations should ensure that they are aware of and adhere to all applicable:
- Laws
- Regulations
- And industry standards that pertain to their operations
The legal category also involves monitoring and addressing legal obligations related to areas such as environmental protection, health and safety, intellectual property, and data protection.
Technical
The technical category focuses on the specific technical aspects and requirements of the ISO standard relevant to the organization’s industry or sector. This can vary widely depending on the standard being audited.
For example, ISO 9001 focuses on quality management, ISO 14001 on environmental management, and ISO 27001 on information security management. In this category, businesses must ensure that they have implemented the necessary:
- Technical controls
- Processes
- And documentation to meet the standard’s criteria
Skills management software and ISO audit preparationCopied
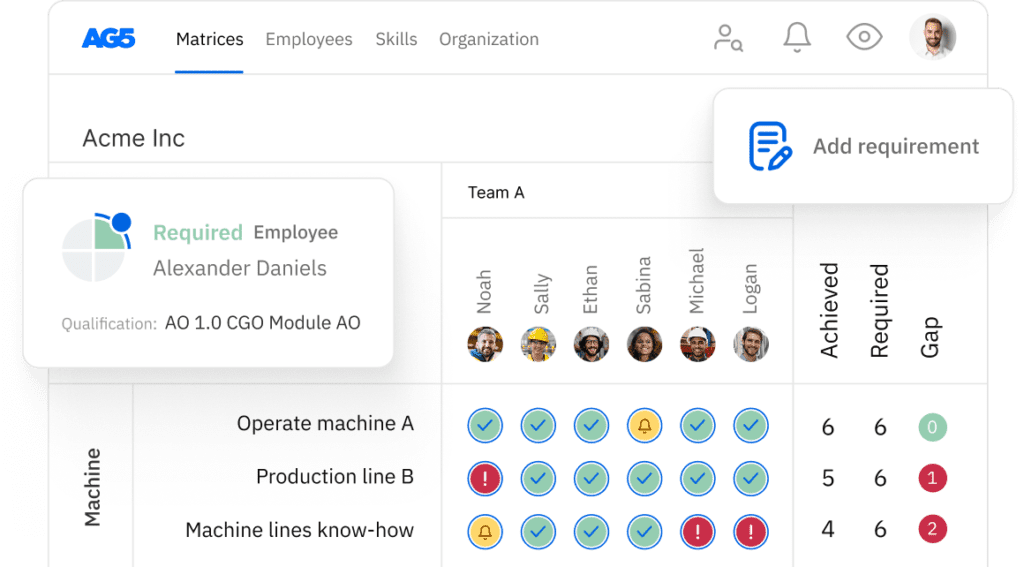
The right skills management software will provide you with a centralized hub of all the skills- and compliance-related information you will need to effectively prepare for an ISO audit.
For example, with its easy to understand and use platform, AG5 provides you with full oversight of the skills, certifications, and qualifications your employees possess – as well as those they will need for any given ISO standard.
Additionally, we provide numerous free certification guides for various certifications, including many ISO certifications. For the full list, visit the “Certification Guides” section of our website.
Ready to see AG5 in action? Book a free, live, 15-minute demo today to see how AG5 can streamline skills management – and the ISO audit process – in your organization.
Resources Copied
Sources Copied
- Change view: Table
-
APA
| # | Source title | Description | Publication | Retrieved | Source URL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Economic benefits of standards | ISO | - | April 22, 2024 | https://www.iso.org/files/live.. |
| 2 | Benefits of standards | ISO | - | April 22, 2024 | https://www.iso.org/benefits-o.. |
| 3 | Obtaining ISO Certification: Practical Tips | Forbes | - | April 22, 2024 | https://www.forbes.com/sites/f.. |
Author Copied
Revisions Copied
Written by: Rick van Echtelt
Copy edited by: Adam Kohut