The EU pay transparency directive: What you need to know
The new EU pay transparency directive will start in 2026, but the preparation for it has already begun. How will the The EU pay transparency directive transform manufacturing in Europe, and how can you best prepare for this? We will go through the most important information in this article.

Equal pay for equal work is set to become a legal requirement in the EU [1], where the gender pay gap currently sits at 13%. The EU Pay Transparency Directive puts in place a framework that aims to eliminate gender-based pay discrimination by way of pay transparency. It also results in potentially far-reaching and costly consequences for businesses that fail to adhere to its standards [2].
This may raise quite a few questions for business leaders. Among them:
- What is pay transparency, and why is it important?
- What is the EU Pay Transparency Directive?
- What does it mean for your organization?
- How does it relate to skills management?
Let’s take a look.
Why is pay transparency important?Copied
Pay transparency is the practice of openly sharing information about employee salaries and compensation – such as pay levels and pay progression structures – within an organization. It promotes gender equality by allowing employees to see how their pay compares to colleagues and industry standards.
Gender discrimination is already illegal in EU member states, the US, and many other countries. However, without measures to provide transparency into pay, discrimination can more easily occur – and be difficult to prove when it does.
Pay transparency decreases gender discrimination by exposing wage disparities. When salary information is openly and publicly shared, it becomes evident if women are paid less for similar roles. This transparency promotes accountability and encourages employers to address and rectify such inequalities, ultimately leading to fairer compensation for everyone.
What is the EU Pay Transparency Directive?Copied
The EU Pay Transparency Directive is set to ensure “equal pay for equal work” in all EU member states. It was adopted in March 2023 by the European Parliament. EU member states have three years to translate the directive into national law.
Under the EU Pay Transparency Directive:
- Employers must offer salary-related information, such as salary ranges, pay levels, and pay progression structures, to current and potential employees
- Employers with more than 100 employees are obligated to report information related to gender pay gaps
- Companies with gender pay gaps of more than 5% are required to take action by way of a “joint pay assessment” in conjunction with workers’ representatives
Organizations bear the burden of proof regarding adherence to the directive’s standards, and face the risk of costly penalties and fines should they be found in infringement.
How ‘equal pay for equal work’ affects businessesCopied
The EU Pay Transparency Directive is fundamentally rooted in the principle of “equal pay for equal work or work of equal value.”
To achieve this, “equal work” must be an objective assessment.
Under the directive, the criteria to make this assessment must include the following four factors:
- Skills
- Effort
- Responsibility
- Working conditions
The directive places pressure on organizations to not only provide equal pay, but to prove it. In most cases, then, organizations will face challenges in demonstrating compliance, regardless of whether they adhere to the directive’s standards.
Now here’s the really interesting part:
“As not all factors are equally relevant for a specific position, each of the four factors should be weighed by the employer depending on the relevance of those criteria for the specific job or position concerned,”
the directive states [3].
This means that, for some organizations – especially those with high numbers of frontline workers – skills will be an extremely important determinant of equal pay.
The importance of skills as a determinant of equal payCopied
Because skills are one of the four mandatory criteria for determining equal pay for equal work, it is more critical than ever that companies have a manner in which to track them. Few organizations, however, have an up-to-date overview of the skills their employees possess and need – as well as how employees stack up to the skills they’re expected to have and develop.
Part of the reason for this is that job descriptions and skill requirements based on job roles are often a poor reflection of reality, especially on the production floor or other environments in which frontline workers are common. Different operators or technicians in the same plant, for example, can perform entirely different work on a day-to-day basis – but good luck capturing that in an HR system.
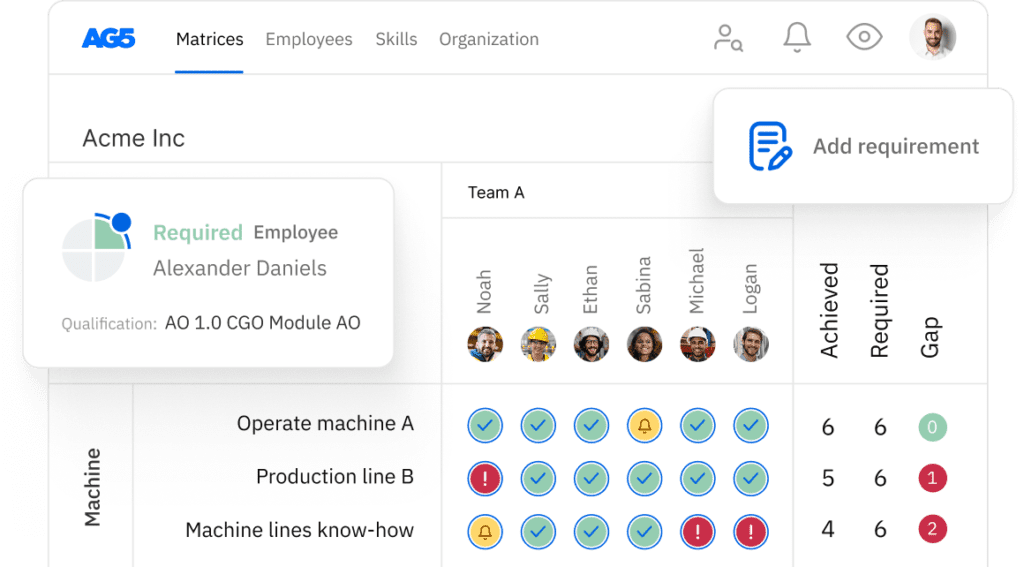
Granted, in process-driven, blue collar-dominant industries that work with Lean or Six Sigma, skills matrices are commonplace – and critical tools organizations use to stay compliant and keep business operations running [4].
But all too often – and because they predominantly take the form of complicated and cumbersome Excel sheets – these skills matrices are not easy to use or manage, and not nearly as effective as they hold the potential to be. Additionally, many skills matrix spreadsheets are not suited to satisfy the standards set in place by the EU Pay Transparency Directive.
This is due to multiple factors, such as:
- There are often dozens of Excel spreadsheets circulating in any given factory or plant, all of them slightly different.
- Skills management systems are often incredibly siloed, with neither employees nor upper management possessing a full understanding of the status of any particular team, much less the entire organization, in terms of current and needed skills.
- Like any spreadsheet, Excel skills matrices are usually not up to date and/or riddled with errors.
A skills management system for the EU Pay Transparency DirectiveCopied
To set up a structure in which skills are determinant of equal pay, you’ll either have to manage a high number of complicated, out-of-date spreadsheets – or implement a skills management software.
The right skills management software for the EU Pay Transparency Directive should:
- Provide a high-level overview of skills-related data to HR and senior management.
- Enable easy, intuitive access and use for line managers, training coordinators, and employees data quality starts on the shop floor.
- Go beyond job roles, with the skills management system itself as closely as possible mimicking the overall organization’s current structure and processes.
During the implementation of such a skills management system, you’ll need to objectively determine explicit skills requirements, then map to them the skills employees already possess. This will also provide you with a deep understanding of the skills your organization needs. Finally – and to fully align with the EU Pay Transparency Directive – you’ll have to link skills to pay.
How can AG5 help you prepare for the EU Pay Transparency Directive?Copied
Reporting obligations for the EU Pay Transparency Directive don’t begin until 2026 [5], but there are several reasons why your organization would be wise to act sooner. Let’s take a look at a few of the benefits that organizations using AG5’s skills management software to increase pay transparency enjoy.
Boosted productivity, flexibility, and efficiency
Companies that use AG5’s skills management software report boosted workforce flexibility and Quality, Health, Safety, and Environment (QHSE) metrics.These companies also improve on operational metrics such as availability, reliability, and productivity. Additionally, they save their line and HR managers hours a week in non-value-added work.
Increased talent retention
Talent retention is a major issue for approximately 66% of the companies we speak with – and their employees often mention they don’t have a sense of career progression in their roles.
Companies that have insight into the skills needed in the organization, make that insight visible to employees – who are then able to tie it to individual career paths – often notice higher rates of employee retention.
Skills management software makes skills tracking and achieving pay transparency much easier, but setting up the structures and onboarding your employees still takes time. Of course, you’ll have the support of AG5 experts here, but this still requires an investment on your organization’s part.
Furthermore, skills management is only step one. Harmonizing skills with pay scales is phase two of compliance with the EU Pay Transparency Directive. You should give yourself ample time to get this done. Proactivity here is not just wise in terms of time management, it can also help you avoid fines, penalties, or other legal issues.
Ready to get started? Request a free, live, 30-minute demo today to see exactly how AG5 can help you revolutionize skills management in your organization – and help you prepare for the EU Pay Transparency Directive.
Sources Copied
- Change view: Table
-
APA
| # | Source title | Description | Publication | Retrieved | Source URL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pay transparency in the EU | European Council | - | April 29, 2024 | https://www.consilium.europa.e.. |
| 2 | Pay transparency in the EU | EU Council | - | April 29, 2024 | https://www.consilium.europa.e.. |
| 3 | EUROPEAN DIRECTIVE TO ENHANCE GENDER EQUALITY IN PAY | De Brau | - | April 29, 2024 | https://www.debrauw.com/articl.. |
| 4 | PWC | EU Pay Transparency Directive enters into force | - | April 29, 2024 | https://www.pwc.nl/en/insights.. |
| 5 | How to best prepare for the recently adopted EU Directive on Pay Transparency? | EY | - | April 29, 2024 | https://www.ey.com/en_ch/workf.. |
Author Copied
Revisions Copied
Written by: Rick van Echtelt
Copy edited by: Adam Kohut