Calibration skills matrix template
A skills matrix template is a tool teams can use to effectively manage and assess their calibration skills and knowledge.
Download your free template here
Overview Copied
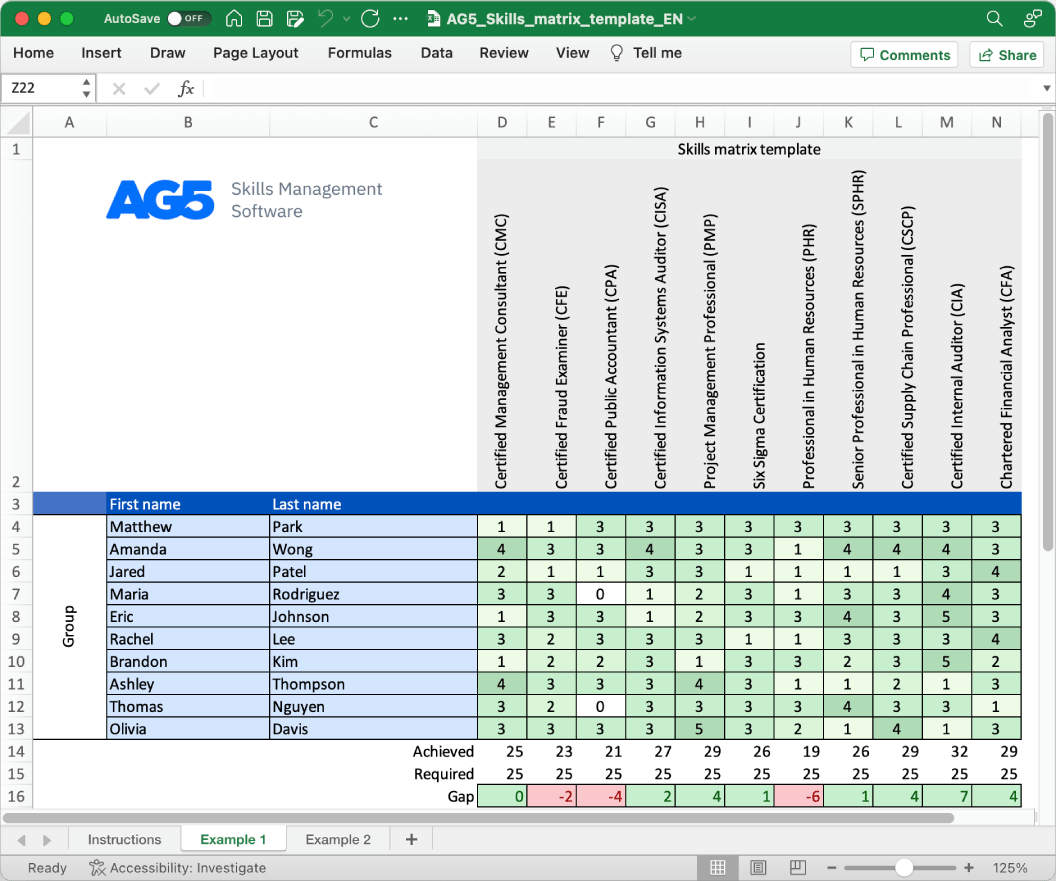
With our free calibration skills matrix template, you will receive a clear overview of the skills that are present in your organization, as well as those that are missing. Using this information, you can develop and implement a plan to ensure that your employees’ skills in calibration are up to date, comprehensive, compliant, and ready for the future.
- Certified Calibration Technician
- Certified Calibration Specialist
- Certified Calibration Engineer
- Certified Metrologist
- Certified Measurement and Calibration Technician
- ISO/IEC 17025 Lead Assessor Certification
- Certified Calibration Auditor
- Certified Calibration Laboratory Manager
- Certified Calibration Trainer
- Certified Calibration Program Manager
- Certified Uncertainty Analyst
- Certified Calibration Data Analyst
- Certified Calibration Software Specialist
- Certified Calibration Quality Assurance Specialist
- Certified Calibration Process Improvement Specialist
- Certified Temperature Calibration Specialist
- Certified Electrical Calibration Specialist
- Certified Pressure Calibration Specialist
- Certified Dimensional Calibration Specialist
- Certified Flow Calibration Specialist
Benefits Copied
Skills management software plays a crucial role in calibration by facilitating the tracking and management of skills related to calibration processes. It ensures that personnel with the necessary expertise in calibration techniques, instrument handling, and adherence to calibration standards are appropriately assigned. This ensures accurate and reliable measurements, maintaining the integrity of data and supporting quality control efforts.
Author Copied
Revisions Copied
Use AG5 to identify skill gaps
Say goodbye to Excel matrices. Start using AG5’s plug and play skill matrix software.
ISO27001 certified Free trial available
