Modern manufacturing: Closing the skills gap
In this article, we talk about modern manufacturing’s contribution to closing the skills gap. It examines the strategies, technologies, and initiatives driving workforce development in this sector.

Jobs or careers in manufacturing have historically been some of America’s most sought-after and well-paying. Yet, amid the global workforce shortage, many manufacturing companies are struggling to fill open positions. According to a Deloitte survey, nearly 83% of manufacturers believe attracting and retaining a quality workforce to be a top challenge. Additionally, nearly 45% of manufacturers said they have had to turn down business opportunities because they did not have enough workers. This shortage is partially due to the perception gaps between the public’s image of manufacturing and the reality of the industry’s current state. In this article, we’ll take a look at how the perception gap influences the skills gap – and how you can address these challenges by promoting advanced modern manufacturing careers.
What is modern manufacturingCopied
Modern manufacturing – also known as advanced manufacturing (AM) – refers to the use of new technology to improve or create new products and processes. Because new technologies are constantly evolving, the manufacturing industry is one in which change occurs with high regularity. Adapting to these changes – and using the new technologies that come along with them – enables companies to stay competitive, relevant, and successful.
What is the perception gap in the manufacturing industry?Copied
The perception gap in the manufacturing industry is a significant challenge to managers today. It refers to the difference between what people think manufacturing is versus what it entails in reality.
On the one hand, many people still perceive manufacturing as labor-intensive. Yet, modern manufacturing has evolved and relies heavily on advanced digital technologies to boost production and efficiency.
High-tech innovations such as 3D printing, machine learning, robotics, and real-time data collection are advancing production processes to meet the growing demand for new products faster than ever.
This digital transformation of the traditional factory floor demonstrates how modernizing this industry is happening at breakneck speed. Yet, despite these advancements, the perception of manufacturing careers hasn’t changed much. This perception gap is one of the causes of the significant skills gap in the manufacturing industry.
Modern manufacturing: Changing the perception of the industryCopied

With 2.1 million unfilled jobs expected by 2030, according to a Deloitte study, the skills gap is a global issue that needs to be addressed. Promoting modern advanced manufacturing careers is one way we can close it. By changing the perception of these careers, and showing young people that they’re interesting, meaningful, and full of opportunity, you can attract top talent to the field and help close the skills gap for good.
How to use advanced modern manufacturing careers to close the skills gapCopied
The skills gap is a significant challenge facing manufacturers today. With an aging workforce and a lack of interest from younger generations, many companies are struggling to find the talent they need to stay competitive. But it’s not all doom and gloom: there are actions manufacturers can take to attract and retain top talent. Here are six ways manufacturers can work toward closing the skills gap.
Rethink your talent pool
The first step in attracting top talent is to rethink your talent pool. Don’t limit yourself to traditional sources like colleges and universities when looking for manufacturing talent. Instead, think outside the box and look for candidates with the right skills, even if they don’t have direct manufacturing experience. This could include veterans, former apprentices, or people currently working in other industries who are interested in a career change.
Get competitive creatively with modern manufacturing
Once you’ve expanded your talent pool, it’s time to get competitive – and we don’t just mean in terms of salary. To attract top talent, you need to offer a competitive benefits package that includes health insurance, retirement savings plans, and paid time off. You should also offer unique perks to make your company stand out from the competition. For example, some companies offer flexible work schedules, tuition reimbursement, and on-site childcare.

Build and strengthen alliances
Another way manufacturers can close the skills gap is by building and strengthening alliances with local schools, community organizations, and government agencies. These relationships can help you raise awareness of modern manufacturing careers and connect you with potential candidates. Manufacturers should also consider partnering with non-competitors to share resources and best practices in their supply chains.
Recruit and promote socially
Social media is a powerful tool that can be used to recruit and promote modern manufacturing careers. Use social media platforms such as LinkedIn, Twitter, and Facebook to post job openings, highlight employee success stories, and promote upcoming events. You can also use social media to connect with potential candidates and build relationships with influencers in your industry.
Boost your current workforce
Your employees are your best ambassadors for attracting new talent. Ask them to spread the word about open positions at your company, or participate in career fairs or other recruiting events. You can also offer incentives for employees who refer qualified candidates, such as cash bonuses or gift cards.
The modern manufacturing smart forceCopied
As the world continues to digitize, the roles and job descriptions in the manufacturing industry are constantly changing. New technologies, for example, have led to the development of new positions to help manage them.
Here, we’ll take a look at a few of the roles within what is described as the manufacturing smart force, a group of highly trained professionals who work with advanced technologies to help companies increase efficiency while reducing costs.
CAM programmer
A CAM programmer is responsible for creating computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) programs that instruct machine tools on fabricating parts from raw materials. This generally involves using 3D modeling software to create a virtual model of the part, which is then used to generate a tool path that will guide the machining process.
CNC machine operator
A CNC machine operator runs computer numerically controlled (CNC) machines, which are computer-controlled tools used to fabricate parts from raw materials. The operator loads the raw material into the machine and runs the program to generate the necessary tool paths to shape the material into the desired part. The operator may sometimes perform quality control checks on the finished parts.
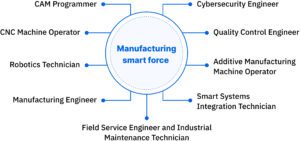
Robotics technician
A robotics technician is responsible for maintaining and repairing industrial robots. This generally involves troubleshooting issues with the robot’s hardware or software, and performing routine maintenance tasks such as lubing joints and replacing worn components. In some cases, robotics technicians may also be responsible for programming robots’ movements or modifying existing programs.
Manufacturing engineer
A modern manufacturing engineer is responsible for designing and optimizing manufacturing processes. This includes developing new ways to manufacture products and improving existing methods to increase efficiency and decrease costs. Manufacturing engineers often use computer-aided design (CAD) software to create models of their proposed processes, which can then be simulated to assess their feasibility.
Cybersecurity engineer
A cybersecurity technician ensures that industrial control systems are protected from cyberattacks. This generally involves identifying vulnerabilities in systems and networks and implementing security measures such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems. Cybersecurity technicians must stay up to date on emerging threats to ensure that their systems are adequately protected.
Quality control engineer
A quality control engineer or technician ensures that manufactured products meet quality standards. This generally involves developing testing methods and conducting inspections at various stages of production. Quality control engineers or technicians also typically write reports detailing their findings and recommending corrective actions when necessary.
Field service engineer and industrial maintenance technician
Field service technicians or engineers are responsible for installing, commissioning, and maintaining industrial equipment at customer sites. This generally requires traveling to customer locations, which can often be remote or challenging. Industrial maintenance technicians are responsible for maintaining industrial equipment in a factory setting. This generally involves performing preventive maintenance tasks, such as regularly lubricating machinery and changing filters.

Additive manufacturing machine operator
An additive manufacturing machine operator runs additive manufacturing machines, which build parts layer by layer from raw materials using computer-generated instructions. The operator loads the raw material into the machine and runs the program to generate the necessary tool paths to shape the material into the desired part. The operator may sometimes perform quality control checks on the finished parts.
Smart systems integration technician
An intelligent systems integration technician integrates industrial control systems with other business systems, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) software. This allows data from different systems to be shared seamlessly, improving efficiency and decision-making across an organization. To effectively perform their jobs, smart systems integration technicians must know about industrial control systems and enterprise software applications.
Skills management in advanced modern manufacturingCopied
Skills management software for manufacturers can help you create skills portfolios for workers and close the skills gap in your organization. By tracking the skills and experience of employees, skills management software enables you to identify gaps when competency mapping and match workers with the training they need to fill them. Additionally, skills management software can help you create a clear career portfolio for each employee, identify potential succession candidates, and invest in your workforce’s development. By using skills management software to its full potential, you can ensure that your workforce has the skills and knowledge they need to meet the challenges of the future.
Do you want to learn more about how skills management software can help you close the skills gap? Schedule your free demo now!