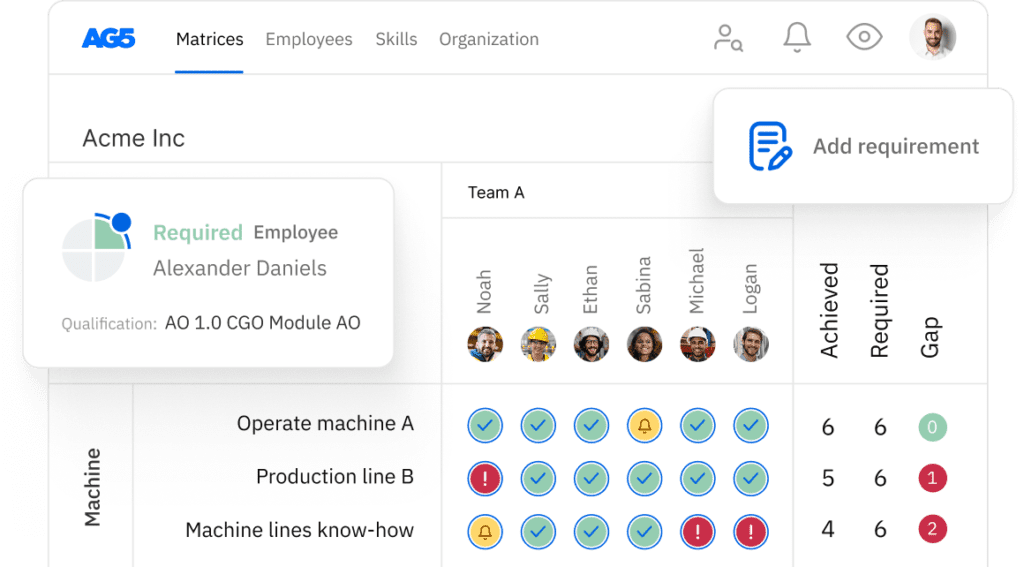
Supplier auditing skills matrix template
A skills matrix is a tool teams can use to effectively manage and assess their supplier auditing skills and knowledge.
Download your free template here
Overview Copied
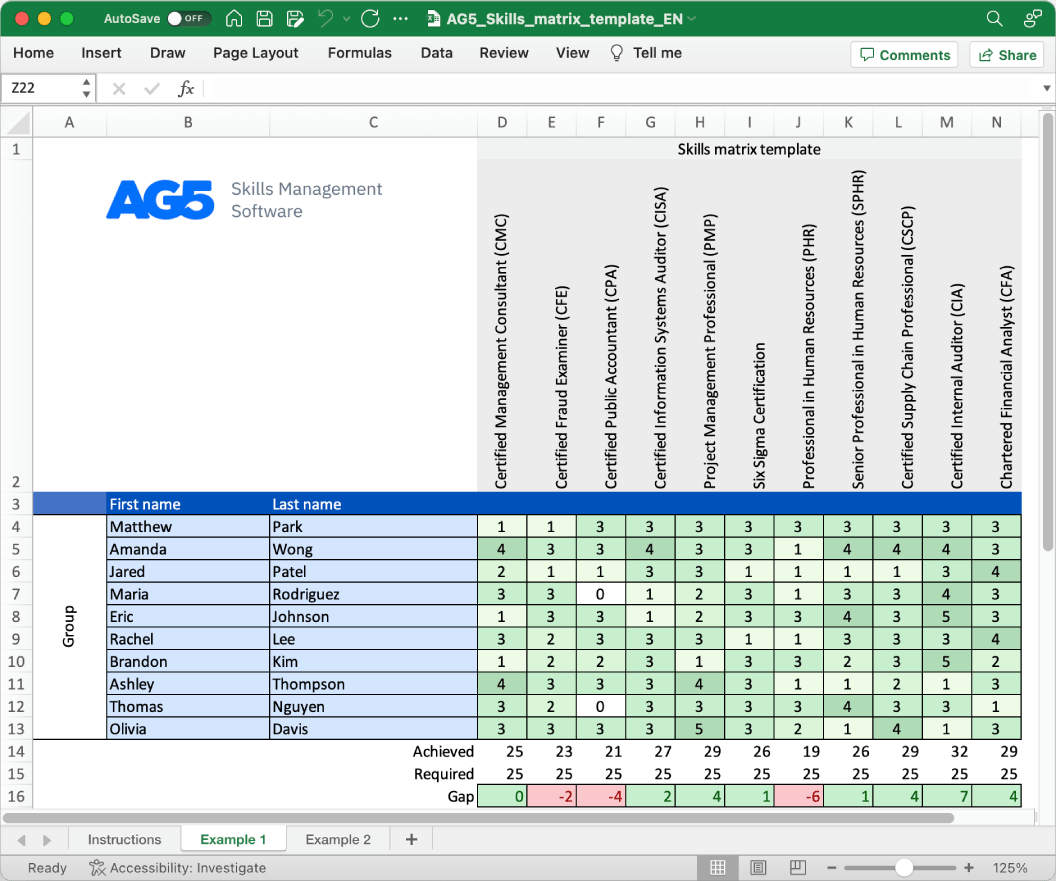
With our free supplier auditing skills matrix template, you will receive a clear overview of the skills that are present in your organization, as well as those that are missing. Using this information, you can develop and implement a plan to ensure that your employees’ skills are up to date, comprehensive, compliant, and ready for the future.
- Certified Supplier Auditor (CSA)
- Certified Supplier Audit Professional (CSAP)
- Certified Supplier Audit Specialist (CSAS)
- Certified Supplier Audit Leader (CSAL)
- Certified Supplier Audit Coordinator (CSAC)
- Certified Supplier Audit Consultant (CSAC)
- Certified Supplier Audit Analyst (CSAA)
- Certified Supplier Audit Trainer (CSAT)
- Certified Supplier Audit Manager (CSAM)
- Certified Supplier Audit Expert (CSAE)
- Certified Supplier Audit Practitioner (CSAP)
- Certified Supplier Audit Team Leader (CSATL)
- Certified Supplier Audit Strategist (CSAS)
- Certified Supplier Audit Improvement Specialist (CSAIS)
- Certified Supplier Audit Quality Professional (CSAQP)
- Certified Supplier Audit Control Technician (CSACT)
- Certified Supplier Audit Governance Specialist (CSAGS)
- Certified Supplier Audit Excellence Analyst (CSAEA)
- Certified Supplier Audit Innovation Practitioner (CSAIP)
- Certified Supplier Audit Transformation Expert (CSATE)
Benefits Copied
Skills management software is important in supplier auditing as it allows organizations to track and manage the skills and qualifications of employees involved in supplier audits, ensuring they possess the necessary knowledge and auditing skills to evaluate supplier compliance with quality and regulatory requirements.
Author Copied
Revisions Copied
Tired of managing skills in Excel?
Say goodbye to Excel matrices. Start using AG5’s plug and play skill matrix software.
Recognized by G2 for Excellence in Skills Management