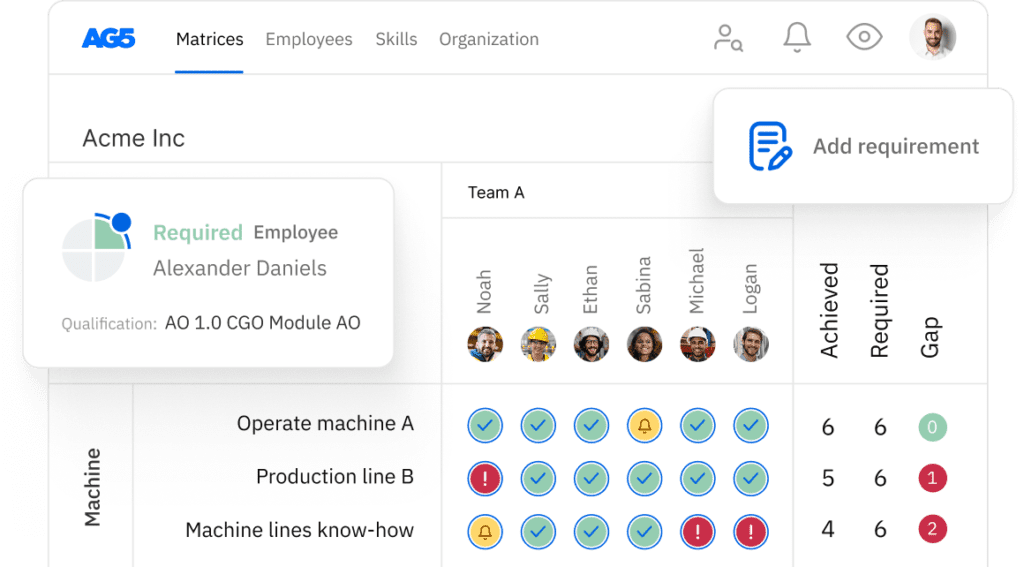
Benefits of standardization in the manufacturing industry
We’ll take a look at the benefits of standardization in manufacturing, offer step-by-step tips to get started, share common pitfalls to avoid when doing so, and more
In the manufacturing industry, it is often extremely important that operational and production processes are reliable and consistent. Standardization is one of the best ways to achieve this. In this article, we’ll take a look at the benefits of standardization in manufacturing, offer step-by-step tips to get started, share common pitfalls to avoid when doing so, and more.
What is standardization?Copied
Standardization is an approach to production that ensures consistency in manufacturing processes – and, as a result, finished products. [1] A standardized approach to manufacturing often involves adhering to industry standards and certification requirements set by a third party, such as those developed by ISO [2]
Standardization is typically achieved by applying a clear set of guidelines and best practices to a manufacturing. This helps ensure that results will always be the same without any loss of quality or productivity, regardless of who is performing the task.
Getting started with standardizationCopied
To get started standardizing your manufacturing processes, you can follow these general steps.
Step 1: Find standards organizations that are relevant to you
You’ll first need to research and find organizations that set industry-wide standards that are related to your manufacturing processes. Some of these standards may be mandatory, while others are voluntary.
Common manufacturing standards organizations include:
- ISO (International Organization for Standardization). International standards that ensure quality, safety, efficiency, sustainability, and more of products and services
- ANSI (American National Standards Institute) [3]. Standards for manufacturing materials, products, systems, and services in the United States
- CEN (European Committee for Standardization) [4]. European standards for various industries in 34 European countries
- SAE International (Society of Automotive Engineers) [5]. International standards for the aerospace, automotive, and commercial vehicle industries
Of course, the above organizations may not apply to you, depending on what you are manufacturing, or the process you are standardizing. But they do give you an idea of the types of standardization organizations with which you may be working.
Step 2: Determine the specific standards that apply to you
After finding the right standardization organization that applies to you, you’ll need to identify the specific standards that are relevant to your organization. You’ll also need to check if there are any legal or regulatory requirements mandating certain standards for your manufacturing processes.
Step 3: Build a standardization team
Next, you can begin creating a team that will implement your chosen method of standardization. When building this team, be sure to include internal experts who possess a deep understanding of your existing processes and products.
Your standardization team should be cross-functional, consisting of employees who work within different areas of your organization, such as:
- Production
- Quality control
- Design
- Logistics
- Safety
This will help you develop a standardized approach that is holistic and comprehensive.
Step 4: Conduct a standardization gap analysis
After building your team, assess your current production processes, then compare them to the requirements set by the standards you wish to adhere to. By identifying gaps – similar to how you conduct a skills gap analysis – you can visualize where you will need to focus.
Step 5: Develop a plan for standardization
Now that you have your standardization team and have conducted a gap analysis, you can begin to develop a standardization plan. Here you’ll need to:
- Define clear objectives regarding what you want or need to standardize – and why you want or need to standardize it
- Establish a timeline for implementing the standards
- Create a budget, then allocate resources for training your employees within your new method of standardization
Step 6: Implement the standards
Implementing standardization is a three-pronged approach that involves:
- Training for employees on the new standards you will implement
- Updating internal documentation to align it with your new method of standardization
- Conducting regular audits of your manufacturing processes to ensure they are compliant with your chosen method of standardization

The benefits of standardization in manufacturingCopied
Standardization has many benefits, especially in manufacturing. [6] Here, we’ll explore six of them.
1. Greater clarity & predictability
Standardization helps you avoid unpleasant surprises in your manufacturing processes. Your processes will become predictable, allowing you to plan and work within them more easily. You will know exactly how they’re configured, the steps that comprise them, and how much time they take. This is reassuring for staff and managers alike, as managers can then steer processes more easily and employees know what the outcomes should be.
2. Knowledge retention
By standardizing processes and tasks, you can more easily document and retain knowledge about your processes. Standardization involves drafting clear instructions, which means it’s far less likely that you’ll lose important knowledge when someone leaves the company, or is off sick. It also helps you onboard new employees more quickly.
3. Greater flexibility
Standardization allows you to be more flexible in terms of building teams and employee rotation. This is because all employees involved in a standardized process will have a clear blueprint to guide them. Additionally, if you standardize products and tools, you can reduce the time needed to find the right replacement components or parts when or if something breaks.
4. Consistent quality
When your employees are completing a task in the same way, your end product will be more consistent in quality. This can help you create an internal method of quality control quality that can help you gain a competitive edge.
5. Regulatory compliance
Most manufacturers have to comply with specific standards set by third-party or governmental organizations. In these cases, standardization acts as a control mechanism to help you comply with rules, regulations, and requirements – and avoid costly penalties or other legal ramifications.
6. Reduced waste
Standardization helps you identify and resolve bottlenecks or other inefficiencies in your production processes. This can result in your organization becoming more efficient with its materials, energy, manpower, and other resources.
Pitfalls to avoid in standardization in manufacturingCopied
When standardizing a manufacturing process, you will need to take steps to avoid pitfalls that may result in delays, inefficiencies, production errors, or lapses in safety. Here are a few common pitfalls you may encounter when implementing a new method of standardization. [7]
- Lack of choice. Standardizing a process may limit product variety. This may work very well for some organizations, but for others – especially those offering custom products, for example – standardization may prove challenging.
- Decreased agility. A commitment to a specific method of standardization may limit your ability to adjust to new technologies or methods of manufacturing. To avoid this, take a flexible approach to standardization that allows for periodic reevaluation.
- Product stagnation. Standardizing a product or process may result in difficulties improving or innovating on them. Again, this may be well suited to time-tested processes or products, but you should also leave room for the integration of new ways of working or technologies.
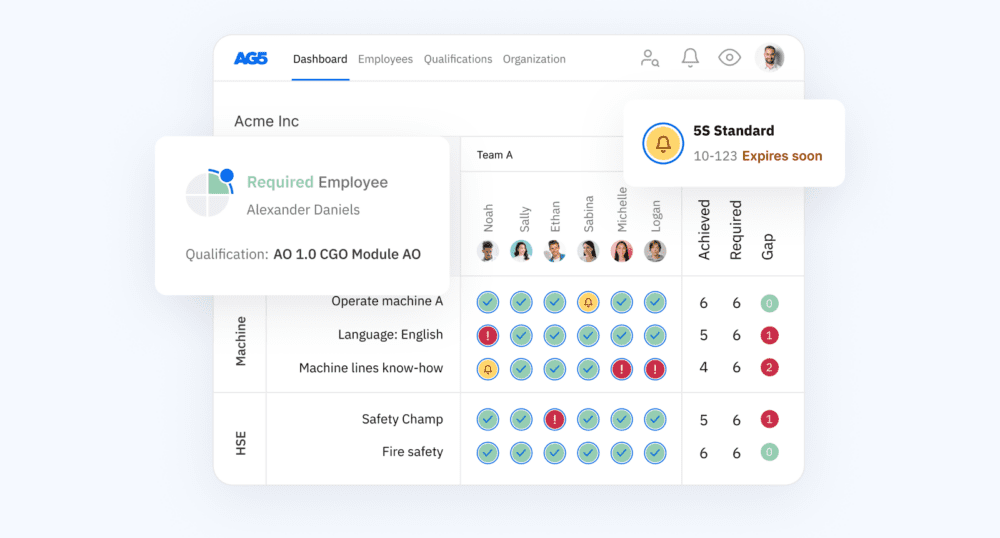
Standardize your production processes with AG5Copied
AG5’s skills management software can help you standardize your manufacturing processes in multiple ways.
With AG5, you can:
- Build cross-functional standardization teams comprised of experts in various departments throughout your organization
- Implement new methods of standardization, then track related training and certifications to ensure that you stay efficient, effective and complaint
- Prepare for standardization-related audits (both internal and external) to ensure that you stay safe and compliant
- And much more
Ready to get started? Schedule a free, live, 15-minute demo for a custom look at how AG5 can help you standardize your manufacturing processes.
Update reason: Added new content, added new sources, refreshed existing content
Sources Copied
- Change view: Table
-
APA
| # | Source title | Description | Publication | Retrieved | Source URL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Standardization in Busines: What It Is and Examples | Indeed | - | May 13, 2024 | https://www.indeed.com/career-.. |
| 2 | International Organization for Standardization | ISO | - | May 13, 2024 | https://www.iso.org/home.html.. |
| 3 | American National Standards Institute | ANSI | - | May 13, 2024 | https://www.ansi.org/.. |
| 4 | European Committee for Standardization | CEN | - | May 13, 2024 | https://www.cencenelec.eu/.. |
| 5 | Society of Automotive Engineers | SAE International | - | May 13, 2024 | https://www.sae.org/.. |
| 6 | 5 reasons standardizing your processes is the best thing you can do for your firm's long-term success | Karbon Magazine | - | April 11, 2024 | https://karbonhq.com/resources.. |
| 7 | What Is Product Standardization? (With Common Uses) | Indeed | - | May 13, 2024 | https://www.indeed.com/career-.. |
| 8 | Standardization in Busines: What It Is and Examples | Indeed | - | May 13, 2024 | https://www.indeed.com/career-.. |
Author Copied
Revisions Copied
Added new content, added new sources, refreshed existing content
Written by: Rick van Echtelt