Semiconductor industry skills matrix template
A skills matrix template is a tool that can be used in the semiconductor industry to effectively manage and assess the skills and knowledge of individual employees or teams.
Download your free template here
Overview Copied
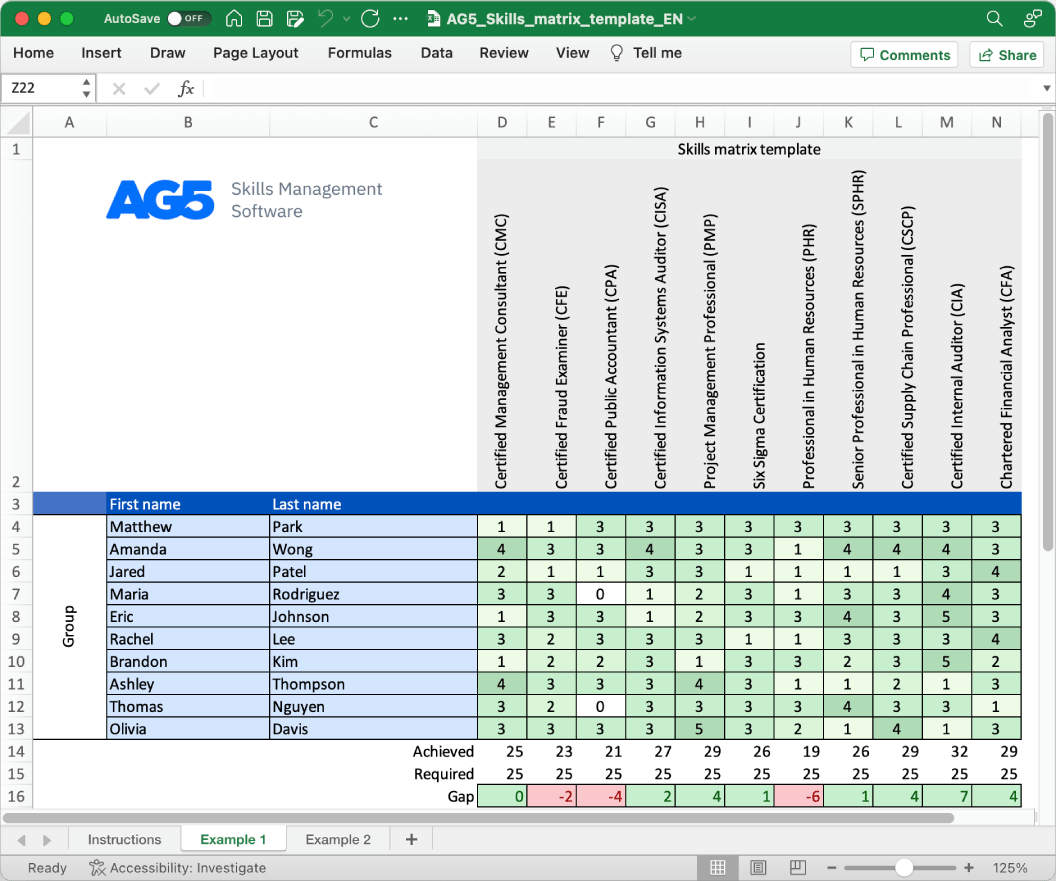
With our free semiconductor manufacturing skills matrix template, you will receive a clear overview of the skills that are present in your organization, as well as those that are missing. Using this information, you can develop and implement a plan to ensure that your employees’ skills are up to date, comprehensive, compliant, and ready for the future.
- Certified Semiconductor Professional (CSP)
- Certified Wafer Fabrication Specialist (CWFS)
- Certified IC Packaging Specialist (CIPS)
- Certified Yield Management Professional (CYMP)
- Certified Test Professional (CTP)
- Certified Equipment Maintenance Technician (CEMT)
- Certified Quality Engineer (CQE)
- Certified Reliability Engineer (CRE)
- Certified Six Sigma Green Belt (CSSGB)
- Certified Six Sigma Black Belt (CSSBB)
- Certified Supply Chain Professional (CSCP)
- Certified Production and Inventory Management (CPIM)
- Certified Manager of Quality/Organizational Excellence (CMQ/OE)
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
- Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC)
- Certified Information Security Manager (CISM)
- Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA)
- Certified Wireless Network Administrator (CWNA)
- Certified Fiber Optic Technician (CFOT)
Benefits Copied
Skills management software can be useful in the semiconductor industry by providing a comprehensive view of employee skills, identifying and managing skill gaps, ensuring proper training, and improving productivity and efficiency in the workplace.
Author Copied
Revisions Copied
Use AG5 to identify skill gaps
Say goodbye to Excel matrices. Start using AG5’s plug and play skill matrix software.
ISO27001 certified Free trial available
