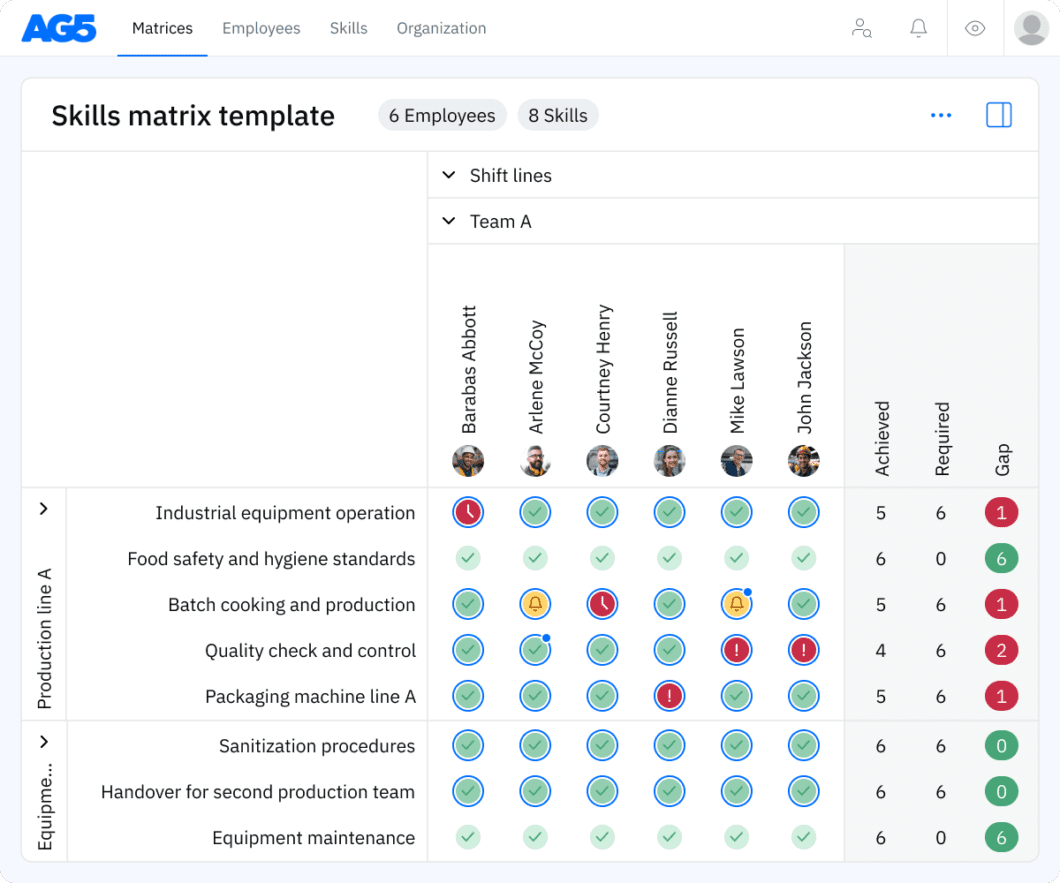
Metals skills matrix template
A skills matrix template is a tool that can be used in the metals industry to effectively manage and assess the skills and knowledge of individual employees or teams.
Download your free template here
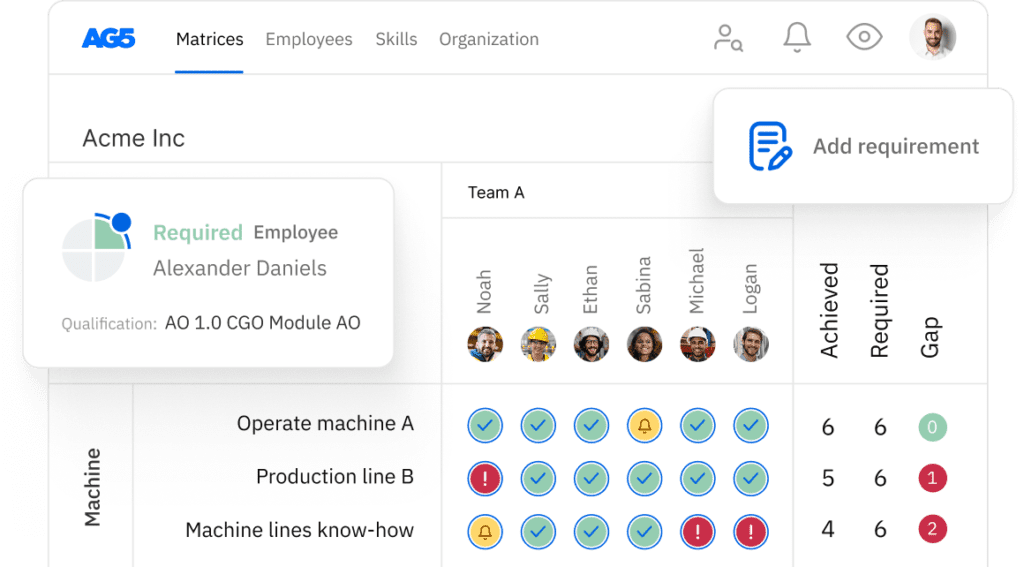
Overview Copied
With our free metals industry skills matrix template, you will receive a clear overview of the skills that are present in your organization, as well as those that are missing. Using this information, you can develop and implement a plan to ensure that your employees’ skills are up to date, comprehensive, compliant, and ready for the future.
Metal fabrication and forming
- Operating metal fabrication equipment such as presses, shears, and roll formers
- Performing welding and cutting operations on various metals (e.g., MIG, TIG, oxy-acetylene)
- Conducting bending, stamping, and forming processes to meet product specifications
- Reading and interpreting technical drawings and blueprints for metal fabrication
- Setting up and adjusting machines for metal fabrication processes
Metal machining and finishing
- Operating CNC machines, lathes, and mills for precise metal machining
- Programming CNC machines for complex metal cutting operations
- Conducting deburring, grinding, and polishing of metal surfaces for smooth finishes
- Measuring and verifying part dimensions using calipers, micrometers, and other precision tools
- Applying surface treatments and coatings (e.g., anodizing, plating) for corrosion resistance
Material selection and properties
- Understanding the properties of different metals (e.g., steel, aluminum, brass, copper)
- Selecting the appropriate metal for specific manufacturing processes and applications
- Identifying metal grades and specifications based on production requirements
- Conducting hardness testing and material strength evaluations
- Evaluating material behavior during processes such as heating, welding, and forming
Quality control and inspection
- Conducting visual and dimensional inspections of metal parts for defects
- Using non-destructive testing (NDT) techniques (e.g., ultrasonic, dye penetrant) to detect flaws
- Implementing Statistical Process Control (SPC) to monitor quality during production
- Documenting inspection results and preparing reports on quality findings
- Performing root cause analysis and implementing corrective actions for quality issues
Benefits Copied
Skills management software can be useful in the metals industry by identifying and managing employee skill gaps, providing a comprehensive view of employee skills, ensuring proper training, and improving safety and productivity in the workplace.
Download the free Excel Metals skills matrix template Copied
We also have a free Excel template available that you can download if you are not ready to get started with AG5. To download it, please complete this form here.
Author Copied
Revisions Copied
Tired of managing skills in Excel?
Say goodbye to Excel matrices. Start using AG5’s plug and play skill matrix software.
Recognized by G2 for Excellence in Skills Management