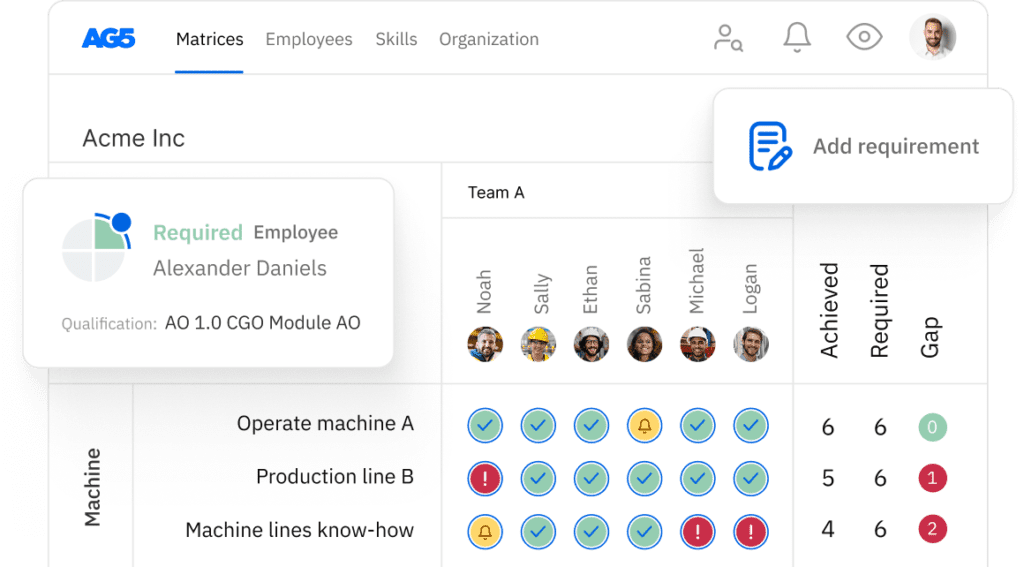
Failure investigation skills matrix template
A skills matrix template is a tool teams can use to assess their failure investigation skills and knowledge
Download your free template here
Overview Copied
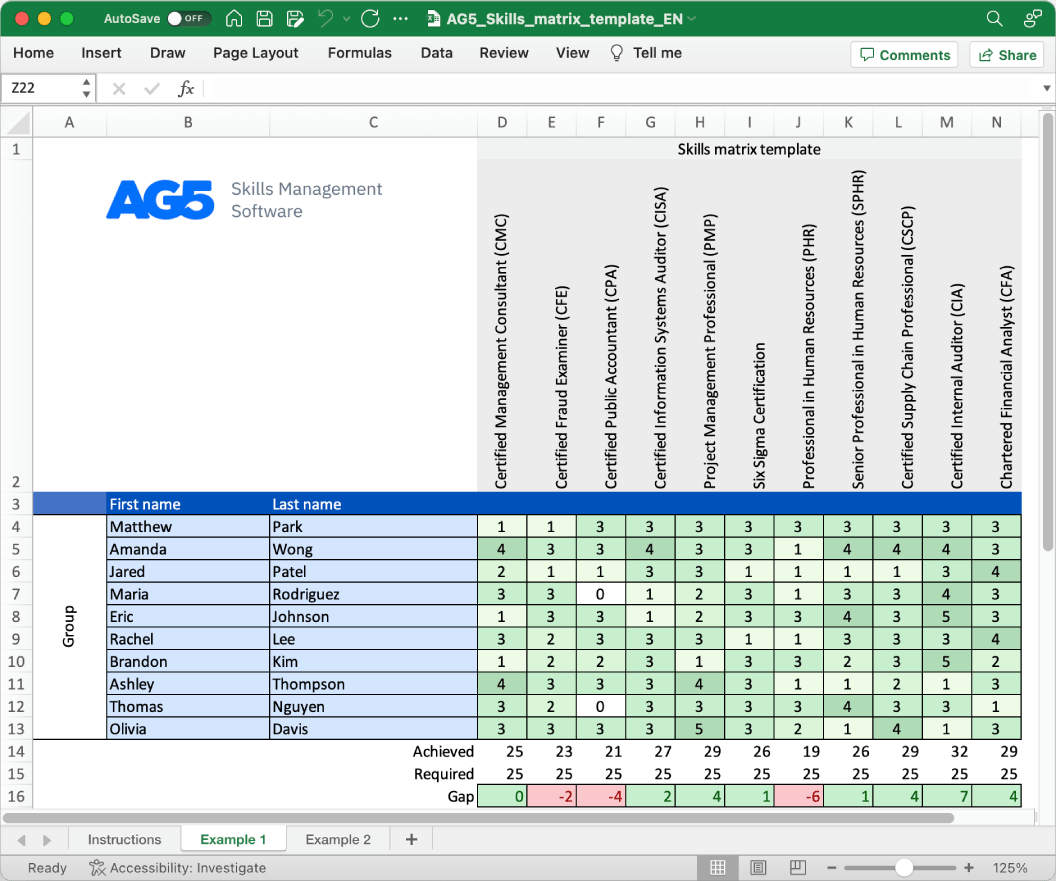
With our free failure investigation skills matrix template, you will receive a clear overview of the skills that are present in your organization, as well as those that are missing. Using this information, you can develop and implement a plan to ensure that your employees’ skills are up to date, comprehensive, compliant, and ready for the future.
- Certified Quality Auditor (CQA)
- Certified Quality Manager (CQM)
- Certified Quality Engineer (CQE)
- Certified Reliability Engineer (CRE)
- Certified Root Cause Analyst (CRCA)
- Certified Root Cause Investigator (CRCI)
- Certified Failure Modes and Effects Analyst (CFMEA)
- Certified Corrective Action Professional (CCAP)
- Certified Problem Solving Professional (CPSP)
- Certified Quality Technician (CQT)
- Certified Failure Analyst (CFA)
- Certified Failure Investigation Analyst (CFIA)
- Certified Failure Investigation Specialist (CFIS)
- Certified Reliability Leader (CRL)
- Certified Reliability Specialist (CRS)
- Certified Reliability Technician (CRT)
- Certified Reliability Analyst (CRA)
- Certified Failure Modes and Effects Analyst (CFMEA)
- Certified Root Cause Analyst (CRCA)
- Certified Problem Solving Professional (CPSP)
Benefits Copied
Skills management software is important in failure investigation, as it ensures the right experts with relevant skills are assigned to investigate and resolve failures promptly, leading to improved problem-solving and product reliability.
Author Copied
Revisions Copied
Tired of managing skills in Excel?
Say goodbye to Excel matrices. Start using AG5’s plug and play skill matrix software.
Recognized by G2 for Excellence in Skills Management