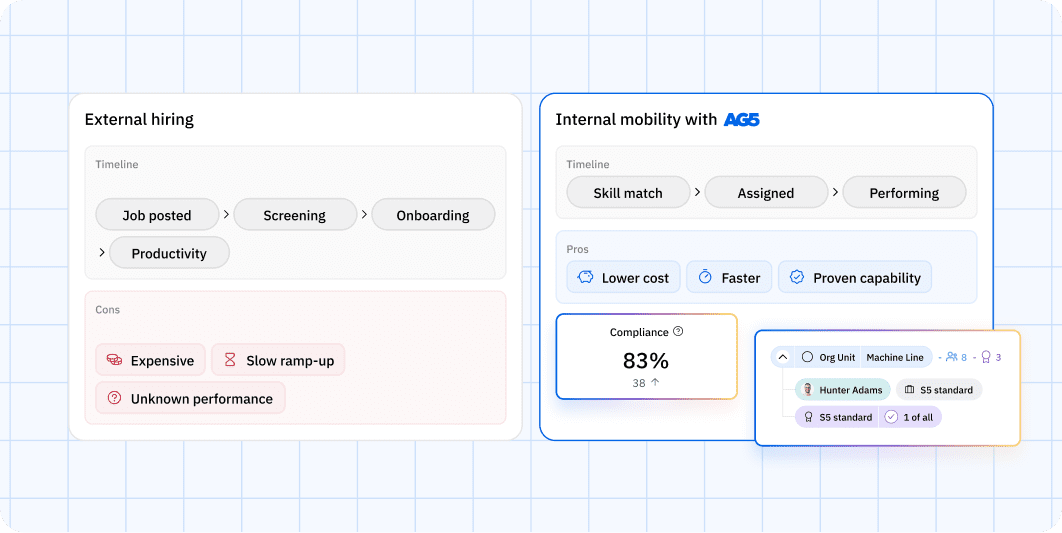
What is talent mobility and why is it critical in 2025?
Talent mobility in 2025 is a strategic imperative driven by skills, enabled by technology, and sustained by culture. It empowers organizations to adapt quickly, retain talent, and unlock hidden potential.
From AI-powered platforms to inclusive practices, mobility has become the cornerstone of a resilient, future-ready workforce strategy.
Talent mobility refers to the strategic movement of employees within and beyond an organization to roles where their skills can deliver the greatest value. In 2025, it is essential for agility, retention, and future-proofing workforce capabilities.
At its core, talent mobility is not merely about filling vacancies-it is about dynamically aligning people’s skills with business needs.
In today’s skills-based economy, the ability to redeploy talent swiftly and intelligently can define an organization’s competitive edge.
In 2025, several forces converge to make talent mobility indispensable:
- Accelerated change in technology and business models means that roles evolve rapidly
- Employee expectations have shifted towards flexibility, growth, and purpose-driven work
- Workforce shortages in critical areas increase the pressure to maximize internal capabilities
Companies with mature mobility programs often see improved engagement, faster innovation, and better succession planning.
Strategic talent mobility enables leaders to spot latent capabilities and apply them where they drive the most impact-whether horizontally into new functions, vertically into leadership, or externally through alumni ecosystems.
Key Drivers in 2025
- AI-driven talent intelligence
- Workforce reskilling at scale
- Shift from role-based to skill-based thinking
- Increased reliance on internal mobility to reduce attrition
How does talent mobility drive organizational agility?Copied
Talent mobility enhances organizational agility by enabling businesses to swiftly align skills with shifting priorities, adapt to market demands, and accelerate innovation through internal redeployment.
In a volatile economic climate, the ability to pivot with precision is no longer a competitive advantage, it is a survival imperative.
Talent mobility sits at the heart of this agility. When organizations treat talent as a fluid asset rather than a fixed resource, they unlock the capacity to respond to disruption with speed and confidence.
Rather than defaulting to external recruitment or costly consultancy, agile firms leverage internal talent marketplaces to match skills to projects, secondments, and new roles.
This not only reduces time-to-productivity, but also increases workforce resilience.
Core benefits of mobility in driving agility
- Reduced lead time in filling strategic gaps
- Increased collaboration across functions and geographies
- Faster learning cycles through dynamic role changes
- Adaptive leadership pipelines for emergent challenges
Case in point: during the COVID-19 crisis, companies with robust internal mobility programs redeployed staff into critical functions overnight – an agility enabled by pre-existing infrastructure and culture.
What is the difference between internal and external talent mobility?Copied
Internal talent mobility refers to moving existing employees within the organization, while external mobility involves sourcing or transitioning talent in and out of the company.
Both approaches support workforce evolution, but have distinct strategic implications.
Understanding the difference between internal and external mobility is vital for designing a balanced talent strategy. Internal mobility focuses on upskilling, redeployment, and career progression within the business.
It leverages known talent, institutional knowledge, and existing culture alignment. External mobility, on the other hand, brings in fresh perspectives, new capabilities, and diversity of thought-but often at higher cost and risk.
In 2025, leading organizations integrate both forms, guided by skills, data and business needs.
However, internal mobility is gaining favor due to cost-effectiveness and its role in employee engagement and retention.
| Feature | Internal mobility | External mobility |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Current employees | New hires or departing employees |
| Speed of deployment | Fast (minimal onboarding) | Slower (requires recruitment & integration) |
| Cultural alignment | High | Variable |
| Cost efficiency | Generally lower | Often higher (recruitment, onboarding) |
| Retention impact | Strong positive influence | Neutral or negative |
| Diversity input | Limited by internal pool | Potentially higher |
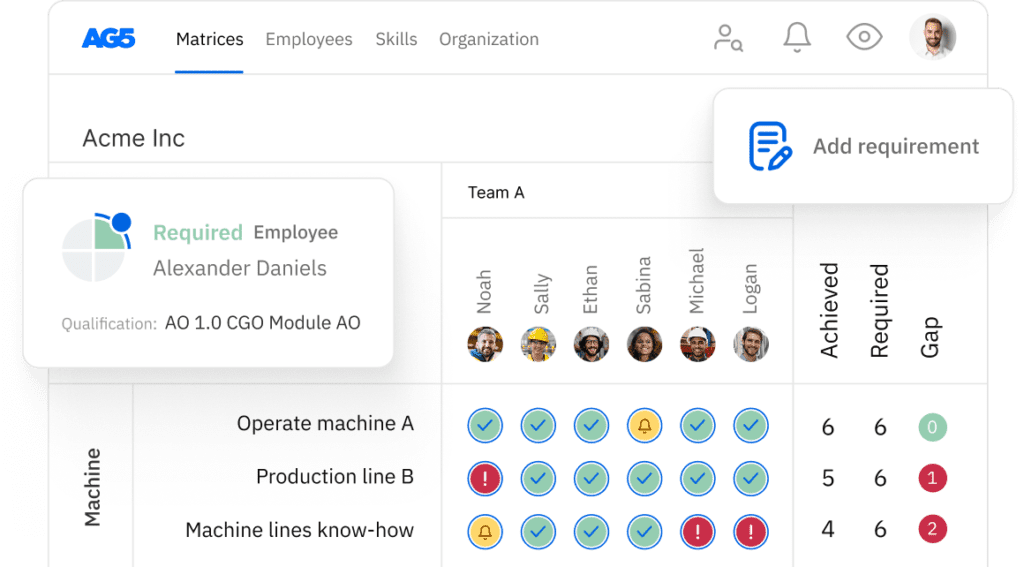
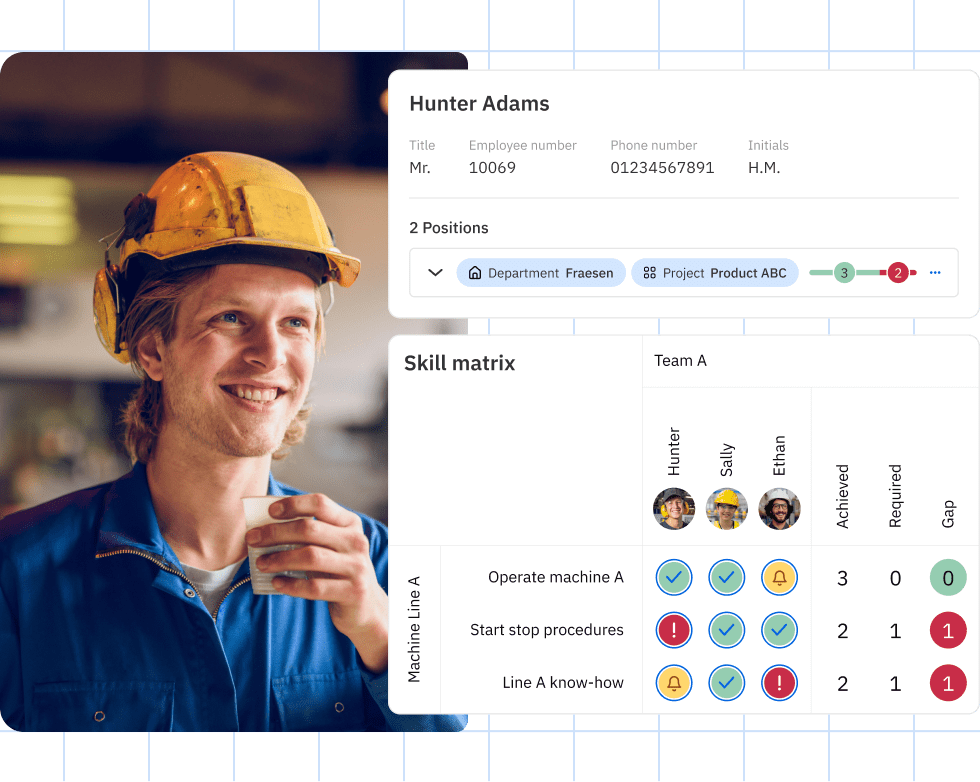
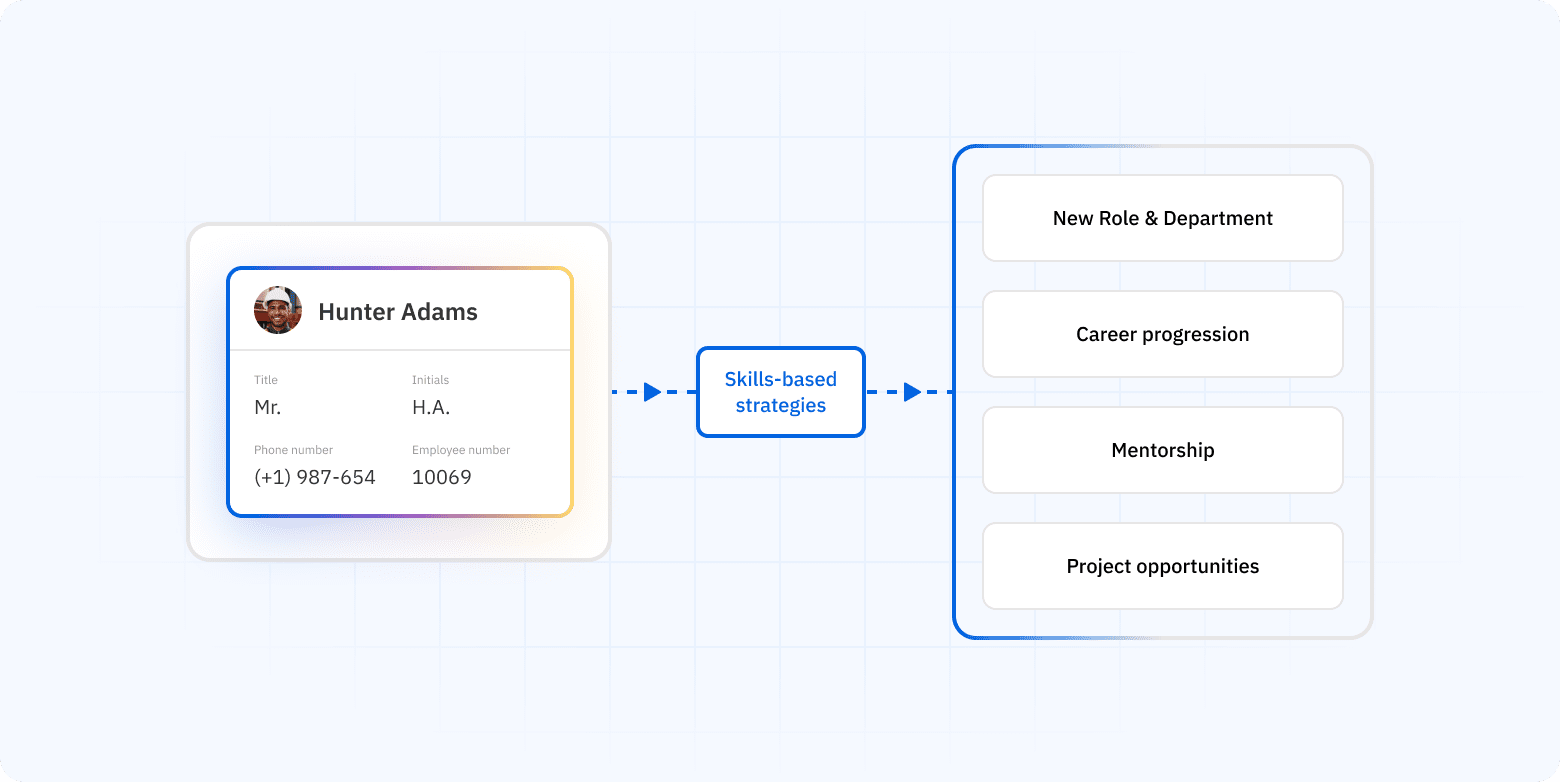
How do skills-based strategies power talent mobility?Copied
Skills-based strategies empower talent mobility by focusing workforce planning on actual capabilities rather than job titles, enabling dynamic deployment, targeted development, and equitable opportunity distribution.
Traditional HR models have long revolved around roles, but in today’s fluid work environment, this structure is proving too rigid.
Enter the skills-based approach – an evolution that places verified, granular skills at the center of workforce architecture. This model allows organizations to identify who can do what, regardless of their current role or job level.
Talent mobility flourishes under this paradigm. Skill management platforms like our proprietary software greatly multiply this mobility.
By mapping employee skills to project needs, training pathways, and emerging roles, companies enable intelligent movement that serves both business and individual growth.
Skills-based strategies also support:
- Transparent career progression through skill-gap identification
- Fairer opportunity distribution, removing biases tied to traditional job ladders
- Faster reskilling, as development is linked to specific business capabilities
- More accurate workforce analytics, informing strategic decision-making
What technologies and platforms enable effective mobility?Copied
Talent mobility platforms use AI and skills data to match employees to roles, projects, and learning pathways – transforming static HR processes into dynamic, responsive talent ecosystems.
In 2025, technology is no longer optional in managing mobility, it is foundational.
The rise of AI-powered talent marketplaces, internal gig platforms, and skills intelligence tools has revolutionized how organizations identify, track, and deploy talent.
These systems use real-time data to understand workforce capabilities, suggest personalized opportunities, and even predict future readiness. For employees, this means greater visibility and control over their career progression. For employers, it offers faster, smarter talent decisions.
| Key enabling technologies | Functionality | Strategic value |
|---|---|---|
| AI-powered talent marketplaces | Match talent to roles, gigs, mentors, learning | Drives internal mobility and agility |
| Skills ontologies | Classify and standardize skills across roles | Enables better analytics and workforce planning |
| Career pathing tools | Visualize growth paths and skill gaps | Empowers employee development |
| Workforce planning platforms | Align talent supply with demand projections | Informs strategy and resourcing |
| LMS with AI integration | Deliver personalized upskilling journeys | Boosts retention and skill acquisition |
Leaders like Unilever, Schneider Electric, and Mastercard have adopted such tools to create self-driven, high-visibility talent ecosystems, resulting in measurable gains in engagement and redeployment speed.
How can organizations build a culture of talent fluidity?Copied
A culture of talent fluidity is built by embedding mobility into organizational values, leadership behaviors, and HR infrastructure, encouraging openness to movement, cross-functional collaboration, and continuous learning.
Technology alone cannot drive talent mobility. The cultural dimension is equally critical. In many organizations, barriers to movement-such as manager reluctance, unclear processes, or fear of poaching-stifle even the most promising strategies.
To overcome this, companies must make mobility a norm, not an exception.
This involves shifting mindsets from talent ownership to talent stewardship, where leaders actively champion employee growth-even if it means movement beyond their team.
| Pillar | Description | Action Example |
|---|---|---|
| Leadership Enablement | Managers supported to release and receive talent | Mobility KPIs for people leaders |
| Psychological Safety | Employees feel safe exploring new roles | Career conversations embedded in check-ins |
| Policy Alignment | HR and operational policies encourage movement | Formalised internal hiring processes |
| Recognition Systems | Success in mobility recognised and rewarded | Celebrating cross-team career moves |
| Skill Transparency | Open access to internal opportunities and skill frameworks | Skills platforms integrated with HRIS |
The result is a more agile, engaged workforce-where employees actively shape their journey, and organizations unlock hidden capabilities from within.
Why is talent mobility key to workforce resilience and retention?Copied
Talent mobility enhances workforce resilience by building adaptable skill sets and improving retention through meaningful career progression and internal opportunity visibility.
In an era where the average tenure is shrinking and skills evolve faster than job descriptions, the ability to redeploy and develop talent internally has become a cornerstone of organizational resilience.
When employees see a future within their company, they are more likely to stay, grow, and contribute in times of change.
Internal mobility satisfies the growing demand for purposeful, personalized career journeys, while reducing reliance on costly external hires.
It also builds redundancy into workforce design-ensuring that when disruption occurs, talent can be reoriented rather than replaced.
Retention metrics from high-mobility companies
| Company | Internal mobility focus | Impact on retention |
|---|---|---|
| Schneider Electric | Internal marketplace & career pathing | 2.5x longer tenure for mobile employees |
| Unilever | Talent-on-demand platform | Increased engagement by 35% |
| IBM | Skills-first internal hiring strategy | Saved $400M annually on external recruitment |
Moreover, mobility signals trust. When an organization invests in growing from within, it demonstrates long-term commitment. This fosters loyalty, motivation, and a willingness to evolve alongside the business.
Do leading companies use talent marketplaces successfully?Copied
Yes, pioneering organizations use AI-powered talent marketplaces to match employees to opportunities dynamically, achieving faster redeployment, improved engagement, and significant cost savings.
Talent marketplaces are no longer experimental. They have matured into a central pillar of workforce strategy for forward-thinking companies.
These platforms use skills data and machine learning to recommend roles, projects, learning, and mentorships to employees, creating a living ecosystem of opportunity.
The most successful implementations are not just technological, but also cultural shifts. They break down silos, reward collaboration, and democratize access to growth.
Company spotlights
| Organization | Platform used | Outcomes achieved |
|---|---|---|
| Unilever | Gloat | 100,000+ gig matches; improved talent retention |
| Mastercard | Eightfold | Reduced time-to-productivity by 50% |
| Nestlé | Fuel50 | Improved employee satisfaction and mobility rates |
| HSBC | Custom AI solution | Enabled 60,000 career moves over two years |
These companies demonstrate that when done right, talent marketplaces are not only efficient-they are transformational.
They serve as engines for mobility, inclusion, and growth in a world where agility is non-negotiable.
How to design and implement a talent mobility strategy in 2025Copied
A successful talent mobility strategy in 2025 requires aligning business goals with skills data, enabling supportive technologies, fostering a mobility-positive culture, and embedding measurable outcomes.
To build a future-proof strategy, organizations must begin with clarity: What are the strategic priorities? What skills will be critical tomorrow?
From there, a cross-functional taskforce – HR, L&D, business leaders, and IT – must collaborate to lay the groundwork for intelligent talent flow.
Step-by-step framework
| Step | Key actions | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Define business needs | Map current and future capability requirements | Clear mobility objectives |
| 2. Conduct skills audit | Assess internal skills inventory using AI tools | Visibility of latent and active skills |
| 3. Select enabling tech | Choose platforms that support matching, analytics, learning | Scalable mobility infrastructure |
| 4. Align policies | Update talent review, hiring, and performance frameworks | Institutional support for mobility |
| 5. Train managers | Equip leaders to identify and release talent responsibly | Reduced resistance to movement |
| 6. Communicate & activate | Launch mobility platform with clarity and motivation | High employee engagement and adoption |
| 7. Measure & optimize | Track success metrics and iterate based on real usage | Continuous improvement and ROI visibility |
The most advanced strategies also include predictive modeling – using AI to forecast mobility patterns and workforce risks, thus enabling proactive talent planning.
What are the common pitfalls and how to avoid them?Copied
Common pitfalls in talent mobility include lack of executive buy-in, poor data quality, manager resistance, and inadequate communication. Avoiding them requires alignment, transparency, and continuous reinforcement.
Despite its clear benefits, many talent mobility initiatives stall or fail due to avoidable missteps. One of the most prevalent is treating mobility as an HR-only program.
Without executive support and business integration, mobility remains underutilized and undervalued.
Equally damaging is the failure to clean and maintain skills data, which undermines AI recommendations and credibility.
A lack of change management, unclear policies, and managers unwilling to “lose” top performers can also cause friction.
Mobility mistakes & how to prevent them
| Pitfall | Impact | Prevention strategy |
|---|---|---|
| No executive sponsorship | Limited resourcing and adoption | Secure C-suite advocacy from the outset |
| Outdated or incomplete data | Poor matching and disengaged users | Use automated tools for skills data upkeep |
| Manager resistance | Talent hoarding and missed opportunities | Train leaders; tie to performance metrics |
| Opaque career paths | Confusion and disengagement | Visualize clear, skill-based progression routes |
| Lack of ongoing communication | Drop in usage and confidence | Keep mobility top-of-mind via campaigns |
A robust strategy anticipates these challenges, building not just platforms but mindsets that embrace flexibility and growth.
Future outlook: Where is talent mobility heading?Copied
Talent mobility is evolving into an AI-driven, skills-first discipline that will underpin workforce architecture, career design, and organizational strategy throughout the next decade.
The future of talent mobility is not just more digital, it’s more human.
As automation transforms tasks and traditional roles fragment, mobility will become the glue that binds evolving capabilities to emergent needs.
This shift will be characterized by hyper-personalization, real-time career navigation, and the seamless integration of learning into everyday work.
Key trends shaping the next phase:
| Trend | Description | Implication for mobility |
|---|---|---|
| AI career co-pilots | Digital assistants guiding growth paths in real time | Highly personalized, always-on mobility |
| Decentralized talent ecosystems | Interconnected networks of internal and external talent | Broader access to skills and flexible resourcing |
| Skills-as-a-service | Portable, verified skills across roles and organizations | Fluid movement between internal and external gigs |
| Inclusive mobility design | Mobility strategies built with DEI as a core pillar | Greater equity in access to opportunities |
| Continuous reskilling loops | On-the-job learning cycles that power progression | Learning as a natural part of mobility |
The most future-ready organizations will shift from reactive deployment to proactive, predictive mobility-driven by data, empathy, and a clear view of both people and purpose.
FAQs Copied
-
What is the main goal of talent mobility?
-
How does talent mobility impact employee retention?
-
What technologies support talent mobility?
-
How do skills-based strategies enhance mobility?
-
What is the role of HR in talent mobility?
-
What’s the difference between vertical and horizontal mobility?
-
Can small organizations implement talent mobility?
-
What are the biggest barriers to effective mobility?
Author Copied
Revisions Copied
Written by: Rick van Echtelt
Copy edited by: Adam Kohut