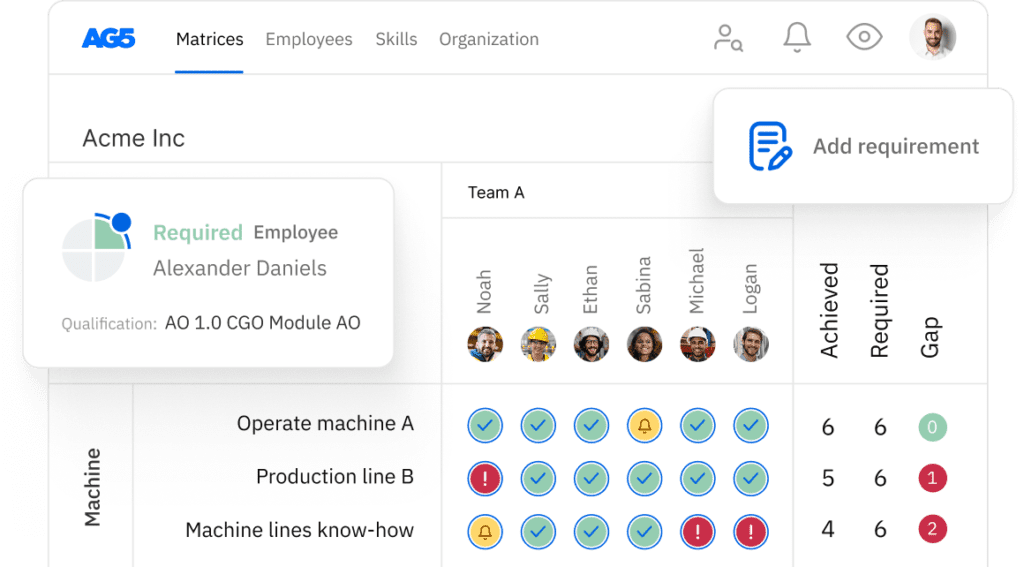
Safety skills matrix template
A skills matrix template is a tool safety teams can use to effectively manage and assess their skills and knowledge.
Download your free template here
Overview Copied
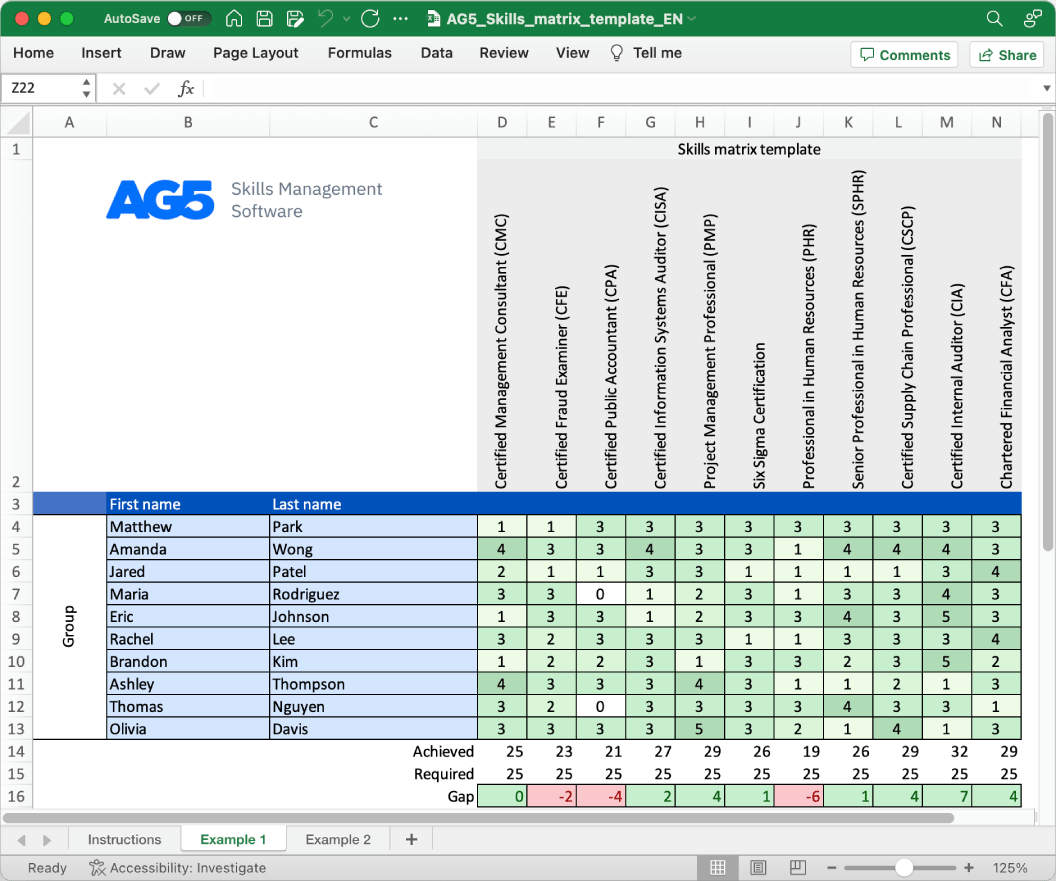
With our free safety skills matrix template, you will receive a clear overview of the skills that are present in your organization, as well as those that are missing. Using this information, you can develop and implement a plan to ensure that your employees’ skills are up to date, comprehensive, compliant, and ready for the future.
- Certified Safety Professional (CSP)
- Occupational Health and Safety Technologist (OHST)
- Construction Health and Safety Technician (CHST)
- Certified Industrial Hygienist (CIH)
- Certified Environmental, Health and Safety Trainer (CET)
- Certified Safety Manager (CSM)
- Certified Hazardous Materials Manager (CHMM)
- Certified Fire Protection Specialist (CFPS)
- Certified Professional Ergonomist (CPE)
- Certified Safety Auditor (CSA)
- Certified Loss Control Specialist (CLCS)
- Certified Safety and Health Official (CSHO)
- Certified Playground Safety Inspector (CPSI)
- Certified Safety and Health Manager (CSHM)
- Certified Product Safety Manager (CPSM)
- Certified Machine Safety Expert (CMSE)
- Certified Construction Safety Manager (CCSM)
- Certified Health and Safety Consultant (CHSC)
- Certified Process Safety Professional (CCPSC)
- Certified Safety Leadership Practitioner (CSLP)
Benefits Copied
Skills management software plays a vital role in safety by tracking and managing employee safety training, certifications, and qualifications. It ensures that employees have the required safety knowledge and skills to perform their tasks safely, mitigating workplace hazards, and maintaining a safe working environment.
Author Copied
Revisions Copied
Tired of managing skills in Excel?
Say goodbye to Excel matrices. Start using AG5’s plug and play skill matrix software.
Recognized by G2 for Excellence in Skills Management