IT security skills matrix template
A skills matrix template is a tool that can be used in IT security to effectively manage and assess the skills and knowledge of individual employees or teams.
Download your free template here
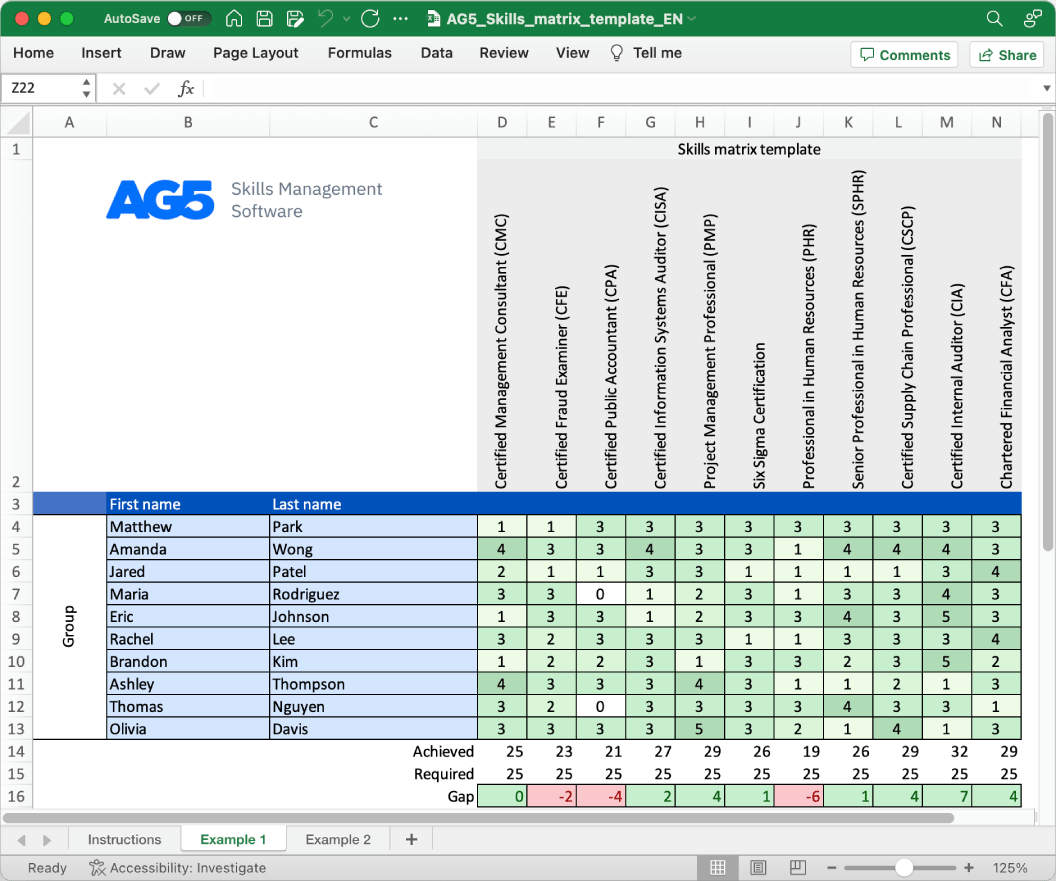
Overview Copied
With our free IT security skills matrix template, you will receive a clear overview of the skills that are present in your organization, as well as those that are missing. Using this information, you can develop and implement a plan to ensure that your employees’ skills are up to date, comprehensive, compliant, and ready for the future.
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
- Certified Information Security Manager (CISM)
- Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC)
- CompTIA Security+
- Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP)
- GIAC Security Essentials (GSEC)
- Certified Information Privacy Professional (CIPP)
- Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA)
- Certified Secure Software Lifecycle Professional (CSSLP)
- Certified Authorization Professional (CAP)
- Certified Penetration Testing Engineer (CPTE)
- Certified Forensic Computer Examiner (CFCE)
- Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP)
- CompTIA Cybersecurity Analyst (CySA+)
- Certified Network Defense Architect (CNDA)
- Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) Security
- Certified Digital Forensic Examiner (CDFE)
- Certified Cyber Forensics Professional (CCFP)
- Certified Information Systems Security Officer (CISSO)
Benefits Copied
Skills management software can help security professionals stay current with the latest threats and vulnerabilities, identify gaps in their expertise, and plan and track progress towards improving their skills.
Author Copied
Revisions Copied
Use AG5 to identify skill gaps
Say goodbye to Excel matrices. Start using AG5’s plug and play skill matrix software.
ISO27001 certified Free trial available
