What is a skills gap analysis?
A skills gap analysis is a strategic tool to future-proof your workforce. It compares current capabilities to future needs using structured models, automated tools, and sector-specific insights.
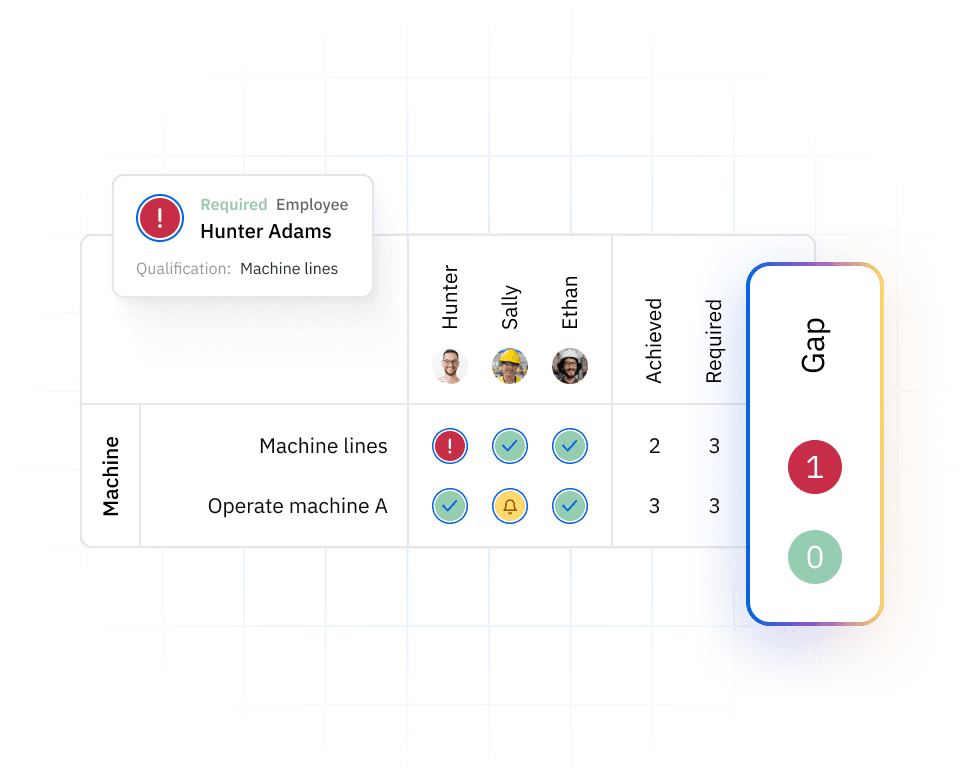
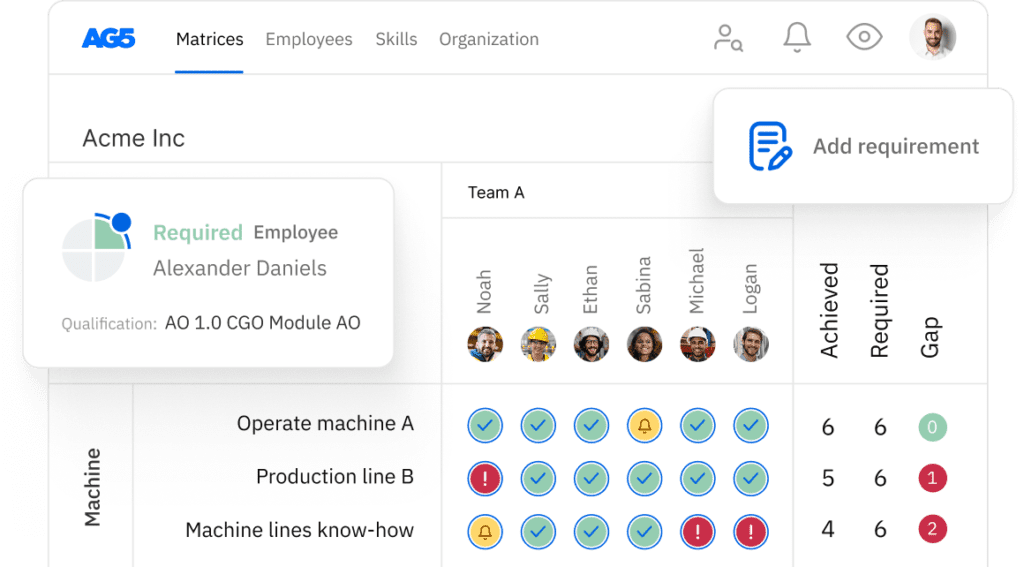
A skills gap analysis identifies the difference between the skills your workforce currently possesses and the skills they need to meet business goals.
It’s a strategic method used to inform talent development, succession planning, and workforce transformation.
Understanding this gap enables organizations to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving marketplace.
With digital disruption, shifting consumer behavior, and labour shortages, businesses can no longer afford to make workforce decisions based on assumptions.
A well-conducted skills gap analysis lays the foundation for upskilling, reskilling, and strategic recruitment.
Key concepts include:
- Current vs. Future State: Benchmarking existing skillsets against strategic objectives.
- Quantitative and Qualitative Assessment: Leveraging both HR data and human insight.
- Strategic Alignment: Ensuring skills development aligns with business KPIs.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Current Skills | Verified skills across departments, roles, or individuals |
| Target Skills | Skills required to meet future demands |
| Gap Size | The magnitude of the shortfall |
| Priority Level | Strategic importance based on role or function |
Next, we explore why this matters even more in today’s business environment.
Why is it important in 2025?Copied
In 2025, skills gap analysis is a strategic imperative for resilience, innovation, and workforce agility.
According to Arizona State University, organizations that fail to anticipate skills shortages risk stagnation [1], non-compliance, and costly misalignment with evolving market demands.
The accelerated pace of change – driven by AI, sustainability targets, demographic shifts, and geopolitical tension – makes annual workforce planning insufficient.
 Skills are becoming obsolete faster than ever, particularly in sectors like logistics and healthcare where automation and regulation are rapidly reshaping roles.
Skills are becoming obsolete faster than ever, particularly in sectors like logistics and healthcare where automation and regulation are rapidly reshaping roles.
Key drivers behind the growing importance:
- Digital transformation: 50% of workers will need reskilling by 2025 (World Economic Forum).
- Labour market volatility: Talent scarcity across technical and frontline roles.
- Regulatory pressure: Especially in healthcare, food safety, and supply chain compliance.
- Consumer expectations: Require adaptive service delivery models powered by skilled labour.
This landscape necessitates proactive, continuous skills analysis to remain competitive and future-ready.
How does a skills gap analysis work?Copied
A skills gap analysis works by comparing existing employee capabilities with the skills required to meet strategic objectives – systematically, department by department or role by role.
It is typically executed in four to six stages, integrating both qualitative input and data analytics.
At its core, the process aims to identify what’s missing, why it matters, and how to close the gap.
This process can be simple for small businesses or complex for enterprises with global operations. However, the underlying principles remain consistent.
What are the key steps in the process?
Each step builds upon the last to ensure comprehensive and actionable results:
- Define Strategic Objectives Understand where the organization is headed – e.g. digital adoption, expansion, regulatory changes.
- Map Required Skills Identify the specific competencies and behaviors required to support those objectives.
- Audit Current Skills Use self-assessments, manager reviews, skills testing, and HR systems to gather data.
- Identify Gaps Compare actual vs. desired skills to locate the deficiencies in capability or capacity.
- Prioritize Gaps Rank by strategic importance, urgency, and impact on business performance.
- Develop Action Plan Define whether to upskill, reskill, redeploy, or recruit – including budget and timelines.
When should you conduct one?
Skills gap analyses should be conducted annually at a minimum, and triggered during key transformation events. Examples include:
- Launching a new product or service
- Integrating new technology (e.g. warehouse automation)
- Regulatory changes (especially in healthcare and food sectors)
- Workforce restructuring or mergers
Best practice: Align the analysis with your annual workforce planning or L&D calendar to drive synergy and budgeting.
What frameworks and models can you use?Copied
Frameworks provide structure, consistency, and depth to skills gap analysis, enabling organizations to move beyond intuition and towards evidence-based workforce planning.
Selecting the right model depends on your organization’s size, maturity, and industry complexity.
How does the McKinsey 7S model apply?
The McKinsey 7S Framework is a holistic model that considers seven interconnected organizational elements: Strategy, Structure, Systems, Shared Values, Skills, Style, and Staff.
It is especially valuable for large enterprises undergoing change, helping ensure that skills are aligned not just to tasks, but to organizational culture and strategic vision.
Use case: In logistics, for example, aligning systems (like warehouse software) and skills (data interpretation, robotics operations) ensures full utilization of technological investments.
| 7S Element | Skills Gap Implication |
|---|---|
| Strategy | Align future skills with organizational goals |
| Structure | Match skill sets to emerging roles and hierarchies |
| Systems | Ensure training supports technology adoption |
| Shared Values | Cultivate cultural competencies and behavioral fit |
| Style | Leadership styles affect coaching and development |
| Staff | Workforce composition informs recruitment needs |
| Skills | Audit and upgrade existing capabilities |
What about the TNA (Training Needs Analysis)?
The Training Needs Analysis (TNA) model is a tactical subset of skills gap analysis, focused specifically on learning interventions. It asks: What must employees learn to close the gap?
It typically includes:
- Organizational Analysis: Why training is needed.
- Task Analysis: What needs to be taught.
- Individual Analysis: Who needs training.
TNA is particularly effective in frontline-heavy sectors like food manufacturing or medical services, where compliance and procedural consistency are critical.
What tools and software help automate the process?Copied
Skills gap analysis software automates data collection, benchmarking, and reporting – making the process scalable, repeatable, and evidence-driven.
It replaces time-consuming spreadsheets with real-time dashboards and integrates with HRIS, LMS, and performance systems.
These tools streamline skill audits, map learning resources, and track progress over time, offering immense value for both HR strategists and operational managers.
Which tools are best for SMEs vs. Large Enterprises?
SMEs typically require simplicity, affordability, and ease of integration:
- Skills Base: Intuitive skill matrix mapping and visual reports.
- iSpring Learn: Combines LMS with gap analysis for training effectiveness.
- Kahoot! 360 for Teams: Engaging assessment tools to gauge frontline skill levels.
Enterprises demand complexity, scalability, and ecosystem integration:
-
- Degreed: Skills intelligence and LXP with analytics.
- Workday Skills Cloud: Deep HRIS integration with AI tagging and recommendations.
- Cornerstone OnDemand: Robust competency management with workflow automation.
| Feature | SME Tools | Enterprise Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Low to Moderate | High (enterprise tiered) |
| Integration Needed | Minimal (LMS/HR-lite) | Extensive (HRIS, ATS, CRM) |
| Scalability | Team to division-level | Organisation-wide, global |
| Analytics Depth | Basic dashboards | AI-powered, predictive |
How do AI-based tools improve efficiency?
AI-driven platforms go beyond static gap identification – they predict emerging skill needs, recommend learning paths, and auto-tag competencies to job roles.
This not only speeds up the process but enhances accuracy and relevance.
Features typically include:
- Natural language parsing of job descriptions and CVs
- Predictive analytics for future skills demand
- Automated skill taxonomies updated via machine learning
In warehousing, for instance, AI can suggest forklift certification or IoT proficiency training based on operational trends and safety data.
How do skills gaps differ across industries?Copied
Skills gaps manifest differently across sectors due to varying compliance requirements, technology adoption rates, and operational workflows.
Industry-specific context is essential when interpreting gap data and designing interventions.
Let us examine four sectors in particular: Food and Beverage, Logistics, Warehousing, and Medical.
Food and Beverage
In food and beverage, gaps often emerge in compliance, digital traceability, and process automation.
Key drivers:
- Stricter food safety regulations (e.g. HACCP, BRCGS)
- Rising demand for digital production tracking (e.g. blockchain)
- Shortage of skilled maintenance and QA technicians
Skill priorities:
- Hygiene protocol adherence
- SCADA and ERP systems literacy
- Lean manufacturing and waste reduction
Practical Tip: Use TNA to ensure HACCP-trained staff are up to date annually.
Logistics
Logistics faces acute gaps in tech fluency, route optimization, and regulatory knowledge.
Key challenges:
- Increased use of fleet management and predictive delivery software
- Pressure to reduce carbon footprint (skills in route planning and emissions reporting)
- Labour shortages in middle-mile and last-mile logistics
Skill priorities:
- Geo-analytics and telematics
- Digital inventory management
- Cross-border compliance (e.g. customs, documentation)
Tool Suggestion: Combine Workday Skills Cloud with transport-specific add-ons like Project44.
Warehousing
Warehousing roles are transforming due to robotics, IoT, and smart inventory systems.
Common gaps:
- Low familiarity with automated picking/packing technology
- Limited data interpretation for demand forecasting
- Safety certifications lagging behind tech rollout
Skill priorities:
- RF scanners and WMS tools
- Warehouse robotics operation
- Health & Safety recertification
Image suggestion: Side-by-side comparison of manual vs. automated warehouse skill profiles.
Medical and Healthcare
Healthcare is experiencing skill deficits in digital systems, remote care delivery, and interdisciplinary collaboration.
Critical areas:
- Adoption of EHR systems and telemedicine platforms
- Communication and empathy in digital interfaces
- Continuous CPD requirements to stay licensed
Skill priorities:
- Data privacy and cybersecurity awareness
- Digital bedside manner
- Clinical documentation and coding (ICD-10)
Regulatory Tip: Ensure alignment with national clinical competency frameworks (e.g. NMC, HCPC).
How do you turn skills gap insights into action?Copied
To convert insights into value, organizations must operationalize their skills gap data through structured, measurable interventions.
This includes aligning development pathways with business goals, securing leadership buy-in, and embedding accountability.
A gap analysis is only as powerful as the decisions it enables. Without execution, it’s a diagnostic with no prescription.
What strategies work best for closing the gap?
Depending on the nature and urgency of the skills shortfall, companies typically pursue one or more of the following strategies:
- Upskilling Enhancing employees’ current capabilities to meet new expectations (e.g. training logistics coordinators on TMS platforms).
- Reskilling Shifting employees to entirely new roles (e.g. retraining F&B workers as quality assurance analysts).
- Redeployment Reassigning talent where gaps exist but training isn’t viable short term.
- Recruitment Hiring externally when speed, precision, or novelty outweigh internal investment.
- Knowledge Transfer Using mentoring or SOP libraries to preserve institutional knowledge and bridge generational gaps.
Action Plan Tip: Map each gap to one of the five responses, assign owners, and define deadlines.
How can you measure ROI?
ROI measurement ensures that training or hiring decisions yield actual performance gains. This includes both leading and lagging indicators:
| Metric Type | Example Metrics |
|---|---|
| Learning Uptake | Course completions, certifications |
| Application Rate | On-the-job behavior change |
| Business Impact | Reduced errors, faster delivery, higher CSAT |
| Financial Return | Cost per hire vs. cost per upskilling |
Use tools like Degreed or Cornerstone to track skills development alongside performance KPIs.
ROI Calculation Formula:
ROI = (Net Benefit from Skill Investment – Cost of Investment) / Cost of Investment × 100%
Why should skills gap analysis be continuous?Copied
Skills gap analysis must be a continuous, dynamic process — not a one-off audit — to remain relevant in the face of constant change.
Static reports become obsolete within months, especially in fast-evolving industries like healthcare and logistics.
Organizations that adopt a cyclical approach to skills diagnostics can pivot faster, optimize talent pipelines, and maintain a culture of proactive development.
Key Reasons for Continuity
- Technological Advancements Automation, AI, and digital tools shift required skillsets regularly.
- Strategic Evolution As goals change — entering new markets, adopting ESG — so do talent needs.
- Employee Turnover Natural attrition disrupts skill continuity. Continuous analysis ensures early detection.
- Market Dynamics Supply chain shocks, regulatory updates, and economic shifts alter workforce priorities.
Best Practice: Integrate skills audits into quarterly OKR reviews, not just annual HR cycles.
Tool Suggestion: Use a talent intelligence platform with real-time skills tracking to automatically surface gaps as roles evolve.
FAQs Copied
-
What is a skills gap analysis?
-
How often should it be conducted?
-
What frameworks are used?
-
What tools automate the process?
-
What’s the difference between upskilling and reskilling?
-
Why do industries have different skills gaps?
-
How do you measure success post-analysis?
-
Is a skills gap analysis only for HR?
Sources Copied
- Change view: Table
-
APA
| # | Source title | Description | Publication | Retrieved | Source URL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | How a Job Skills Gap Analysis Can Help Propel Your Organization Forward | ASU Arizona State University | May 4, 2023 | August 7, 2025 | https://careercatalyst.asu.edu.. |
Author Copied
Revisions Copied
Written by: Rick van Echtelt
Copy edited by: Adam Kohut