Competency management software: Manufacturing industry guide
Throughout this guide, we’ll focus on practical steps: how to define competencies in manufacturing, how to link gaps to training, and how to stay audit-ready. We’ll also reference proven tools such as role-based matrices, certificate tracking, expiry alerts, and HRIS/LMS integrations

Competency management software gives manufacturers real-time visibility into who can operate which equipment, meet which standards, and step into which roles. It enables you to cut defects and downtime, pass audits smoothly, and align training to the skills that matter most.
Manufacturing moves on skills. Yet most plants still rely on spreadsheets that hide gaps, bury certificates, and slow down audits.
Competency management software replaces guesswork with live skills matrices, auditable records, and clear training pathways. For HR, L&D, and operations leaders, it means faster onboarding, safer lines, and consistent quality across shifts and sites.
For frontline teams, it’s simpler: what’s required, what’s current, and what’s next in one place. Throughout this guide, we’ll focus on practical steps: how to define competencies per role and machine, how to link gaps to training, and how to stay audit-ready without fire drills.
Where useful, we’ll reference proven tools such as role-based matrices, certificate tracking, expiry alerts, and HRIS/LMS integrations, so you can scale from a pilot cell to the whole network with confidence.
What is competency management in manufacturing?Copied
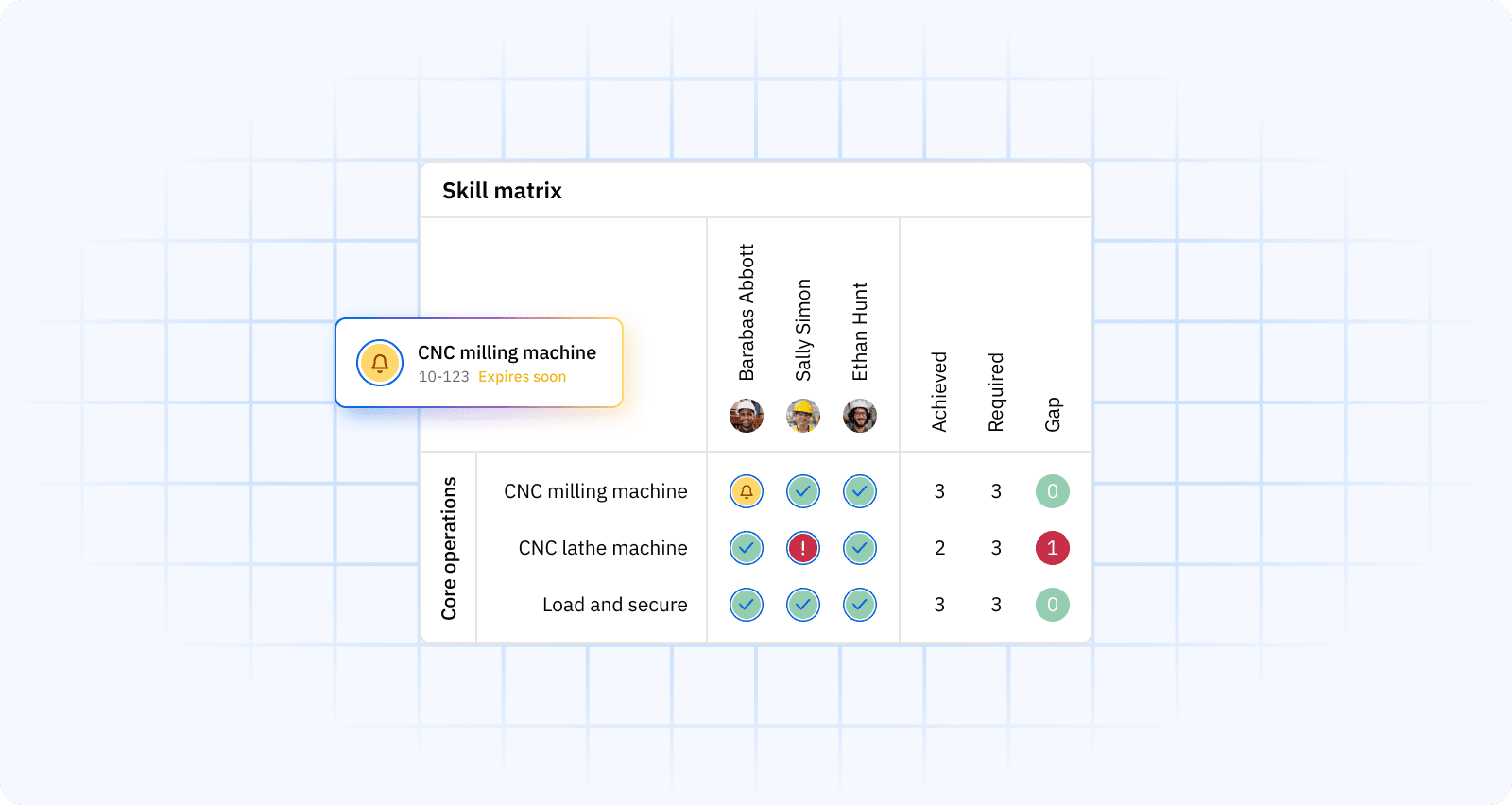
It’s the structured way to define, track, and improve the skills and certifications your production roles require. It is mapped to equipment, processes, and standards using skills matrices, proficiency levels, and auditable records to guide daily staffing and long-term development.
In a plant, competence isn’t abstract. It’s the proven ability to perform tasks at a defined standard under real conditions that include setup, operate, inspect, troubleshoot, and maintain.
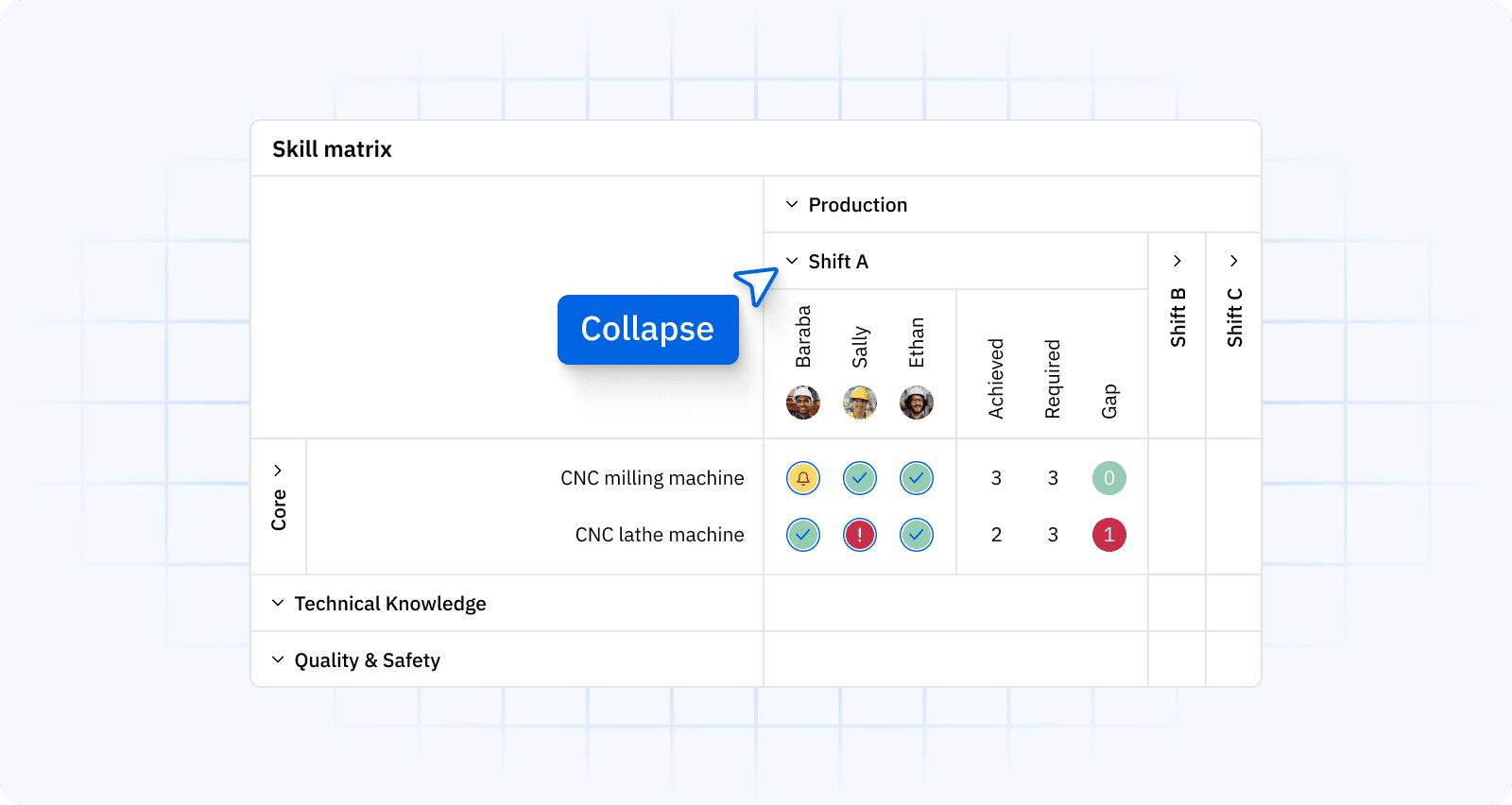
Effective competency management starts by translating job roles into clear requirements and proficiency scales, then visualizing them in a role-based skills matrix. From there, you align training and on-the-job learning to close gaps, while certificate tracking keeps compliance current.
A modern skills management software platform centralizes this: managers see who is qualified for each line, who can be cross-trained, and which certs are nearing expiry.
Practical outcomes include safer changeovers, fewer handoff errors, and faster time-to-competency for new hires. If you need a starting point, grab a skills matrix template and customize it to your processes and machines.
Core components of a manufacturing skills matrix:
-
- Role requirements tied to machines, processes, and standards
- Proficiency scales with observable criteria
- Evidence of competence, including assessments and certificates
- Gap status, target dates, linked training, and owners
Why competency software matters for quality, safety, and complianceCopied
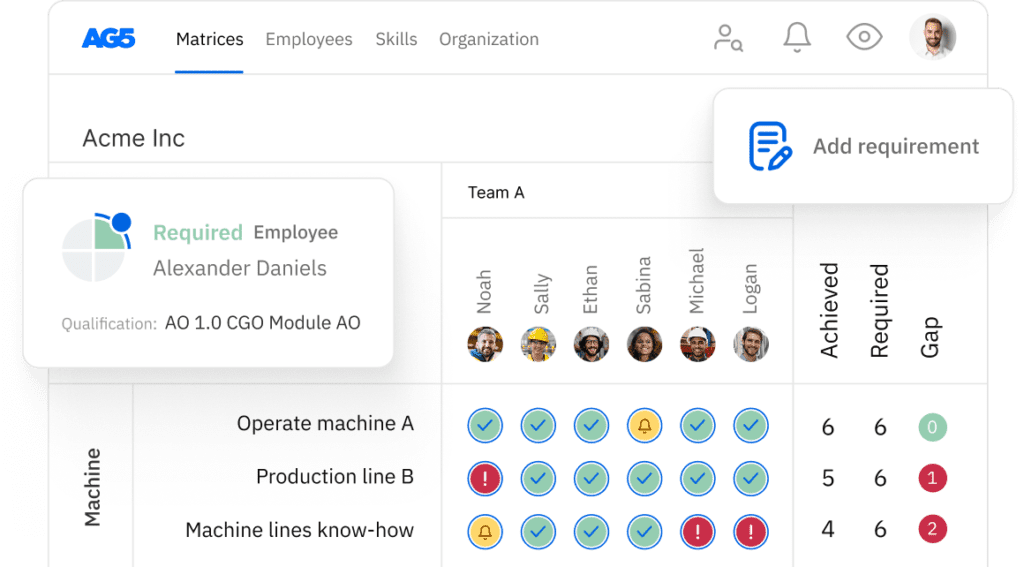
It gives leaders live proof of who is truly qualified, where gaps sit, and which certificates are at risk, so you prevent defects and incidents, meet ISO/IATF/OSHA obligations, and pass audits without last-minute fire drills.
Quality and safety depend on having the right people on the right jobs with the right evidence. Competency software centralizes role requirements, proficiency levels, and certifications, then visualizes them in real time.
Supervisors can staff lines by verified capability, not assumptions. L&D can target training where it closes the biggest risks. Compliance teams can produce auditable records in minutes, not days.
The result is fewer process deviations, faster changeovers, and tighter control over special processes like welding, CNC, and chemical handling. Unlike spreadsheets, a platform maintains a single source of truth with versioning, alerts, and permissions – which is crucial when you run multiple shifts and sites.
Pair this with structured skills tracking and competency gap analysis to move from reactive firefighting to proactive prevention.
What leaders gain:
-
- Single source of truth for roles, skills, and certs
- Real-time gap alerts and expiry reminders
- Faster investigations with auditable histories
| Area | Common issue | Software-enabled outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Quality | Undocumented competence leads to scrap | Lower rework via verified proficiency |
| Safety | Expired permits on critical tasks | Fewer incidents through expiry alerts |
| Compliance | Slow audit evidence collection | Faster audits with complete trails |
Why skills visibility reduces defects and downtime
Visible, verified competence lets you staff by capability and not convenience. It reduces setup errors, rework loops, and unplanned stops across shifts and product variants.
When supervisors see exactly who is certified on which machines and processes, staffing becomes a control mechanism for quality.
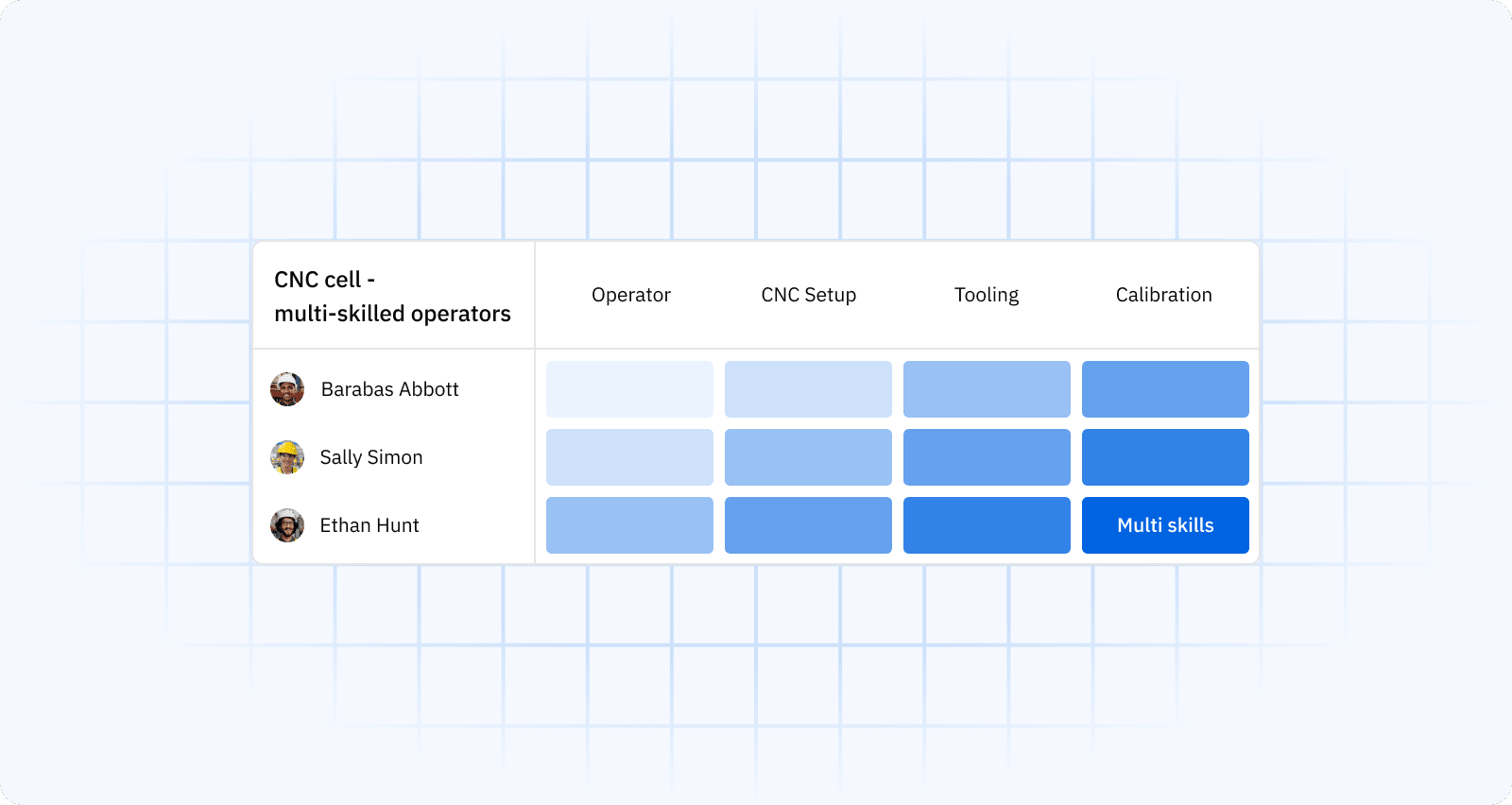
New or complex SKUs no longer land with the least-busy operator, instead they go to proven hands. Cross-training plans are guided by real gaps, so coverage improves without sacrificing standards. Visibility also accelerates changeovers because the right mix of setup, operation, and inspection skills is present at the cell.
Over time, you build depth: more people at higher proficiency on critical tasks. That cushions vacations, attrition, and demand spikes. Crucially, visibility is not just a list of names, it links each skill to observable criteria and evidence, so managers can trust what they see.
Practical levers:
-
- Staff lines by verified proficiency, not seniority
- Prioritize cross-training on bottleneck equipment
- Link gaps to role-specific training and OJT
| KPI | Why it moves |
|---|---|
| First-pass yield | Fewer operator-driven defects after staffing by competence |
| Changeover time | Better skill mix reduces setup errors and retries |
| Unplanned downtime | Fewer stoppages due to mishandled procedures |
Why audits get easier with certificate tracking and logs
Centralized certificate vaults, expiry alerts, and audit trails give instant proof of compliance so you answer auditor requests with complete, timestamped records.
Audits stall when evidence is scattered across inboxes, binders, and spreadsheets. Competency software stores certificates, assessments, and approvals against each person and role, then tracks expiries automatically.
Before an audit, compliance can run prechecks to resolve gaps. During an audit, you can filter by standard, site, or process and download proof packs with signatures and timestamps.
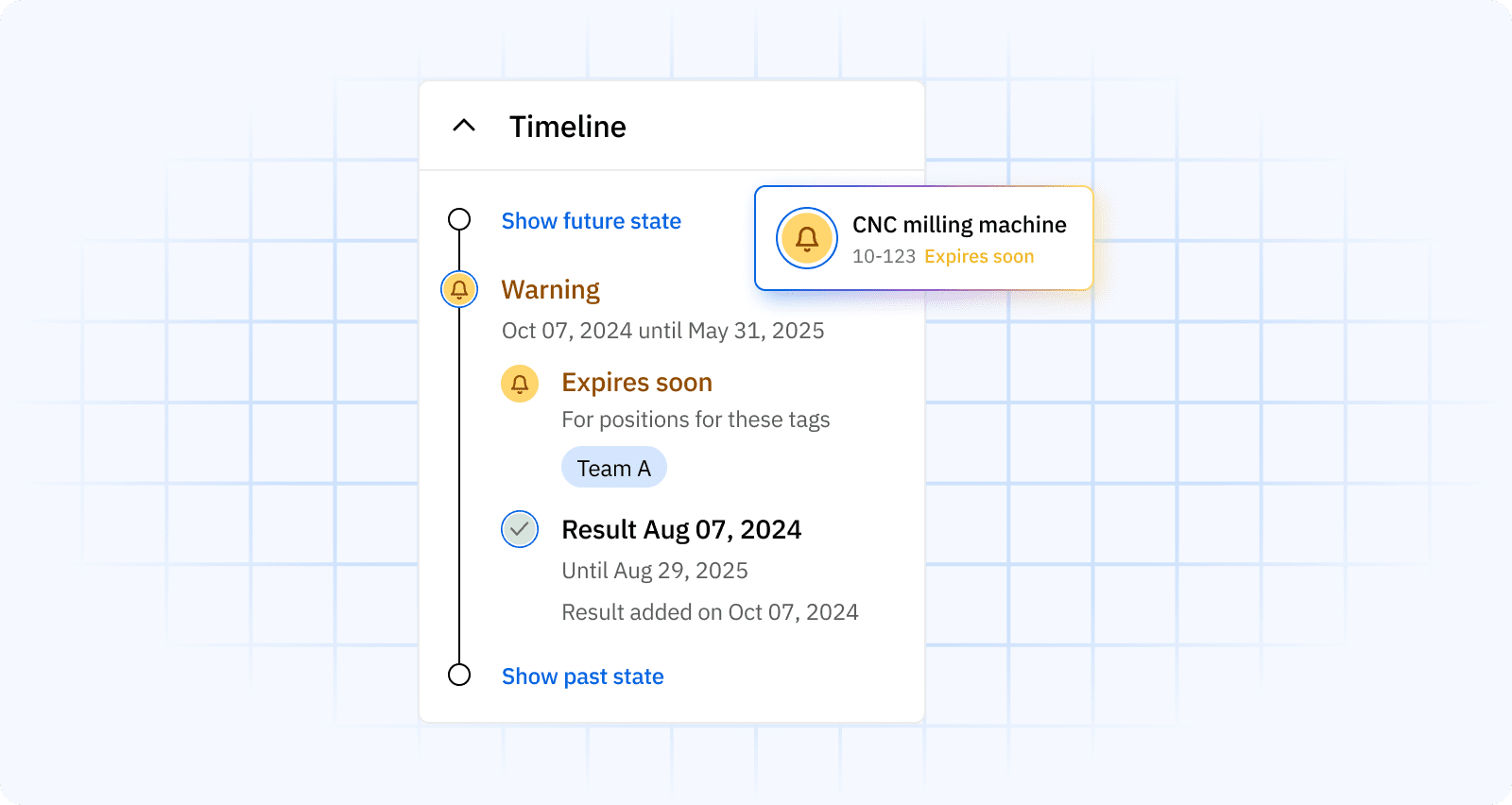
For regulated tasks such as confined space entry, powered industrial trucks, and special process qualifications, alerts prevent people from being scheduled after a lapse. Approval workflows and immutable logs show who assessed whom, when, and against what criteria.
That transparency shortens audits and reduces findings, while giving customers and regulators confidence that your workforce is demonstrably qualified.
What to standardize:
-
- Document types per role and standard
- Reassessment intervals and proficiency scales
- Approver roles and escalation paths
| Evidence | Example |
|---|---|
| Certificate and validity | Operator’s forklift license with expiry date |
| Competence assessment | Signed OJT checklist with criteria met |
| Audit trail | Timestamped history of assessments and approvals |
How competency platforms work in practiceCopied
A modern platform turns role requirements into live skills matrices, links them to evidence and certificates, triggers gap and expiry alerts, and integrates with HRIS/LMS, so supervisors staff by verified capability and L&D closes the right gaps first.
The day-to-day flow is straightforward. You define roles and required competencies, set proficiency scales, and capture assessments, checklists, certificates for people and teams.
The platform visualizes this in a skills matrix with traffic-light status and automated skills tracking. Expiry reminders prevent lapses on safety-critical tasks, and audit logs record who assessed whom, when, and against what criteria.
Integrations keep data current: HRIS provides org and job data, the LMS supplies completions, and the competency system reconciles it into one source of truth.
Mobile access lets frontline teams self-assess, upload proof, and keep records fresh between shifts. Managers then filter by site, cell, machine, or product family to see coverage and plan cross-training.
The payoff is simple: fewer surprises, faster staffing decisions, and leaner audits.
Core building blocks:
-
- Role-based matrices with observable criteria
- Certificate vault with expiry alerts
- Proficiency levels and reassessment cycles
- HRIS/LMS integrations and SSO
How to build and roll out a competency frameworkCopied
Start lean. Define roles, break work into competencies with clear scales, gather acceptable evidence, then pilot on a high-impact area before standardizing across sites with governance and cadence.
Begin with roles that drive quality or safety. Break each role into competencies mapped to machines, procedures, and standards. Write proficiency scales with observable behaviors meaning what a 1, 2, 3, or 4 looks like on the floor and define acceptable evidence such as OJT checklists, supervisor sign-offs, or third-party certs.
Build your first matrix using a skills matrix template, then run a 6–8 week pilot on a safety-critical line to calibrate criteria, cycle times, and reassessment intervals.
Involve supervisors and experienced operators to align the rubric with reality and secure buy-in. After the pilot, standardize naming conventions, documentation types, and approver roles.
Establish a monthly review cadence and an escalation path for overdue assessments.
Finally, scale by site with a governance group that stewards changes, supports audits, and ensures consistency.
Practical steps:
-
- Define 8–12 competencies per role with clear verbs and criteria
- Agree acceptable evidence and reassessment intervals
- Pilot on one line, then standardize naming and workflows
- Roll out with supervisor training and a monthly calibration
| Role | Competency | Proficiency indicator | Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC operator | Setup & tooling | Sets offsets within spec without rework | Signed OJT checklist |
| Welder | Process compliance | Performs WPS per parameter window | Valid WQT/WPS cert |
| QA inspector | Gauge use | Conducts GR&R-compliant checks | Supervisor assessment |
How to align gaps with training and workforce planningCopied
Use gap alerts to trigger targeted courses and OJT, prioritize by risk and cost, and build cross-training plans that protect throughput during demand swings and vacations.
Once gaps are visible, connect each one to a specific intervention including course, micro-module, checklist, or mentoring session and set target dates.
Prioritize by risk to product quality and safety, the cost of the gap, and the time to close it. For bottleneck machines, accelerate cross-training to deepen coverage across shifts. Feed your production plan into the platform to see future coverage by role and line; then schedule training windows that won’t choke capacity.
For new product introductions, map ramp-up skills early and schedule qualifications before PPAP or first-article runs. The goal is a rolling plan where gaps shrink continuously and training spend tracks business impact, not guesswork.
Prioritization levers:
-
- Risk to safety and customer quality
- Cost of non-conformance and downtime
- Time to competence and trainer availability
| Gap risk | Typical action | Review cadence |
|---|---|---|
| High | Immediate OJT + supervised shifts | Weekly until closed |
| Medium | Scheduled course + validation run | Bi-weekly |
| Low | Self-paced module + spot check | Monthly |
How to calculate ROI and select the right platformCopied
Model ROI from fewer defects, faster audits, safer operations, and reduced admin then select a platform on feature depth, integrations, security, and multi-site scalability.
Quantify benefits where money truly moves. On quality, track scrap and rework reductions associated with staffing by verified competence.
On safety, estimate avoided incident costs tied to expired qualifications. For compliance, calculate hours saved gathering audit evidence; for administration, tally time removed from spreadsheet updates and email chases.
Add time-to-competence improvements for new hires. Build a conservative model over 12 months and pressure-test assumptions with pilot data.
For selection, weight must-haves – role-based matrices, certificate tracking with alerts, audit trails, mobile app, SSO, robust APIs – and score vendors on reliability and ease of use.
Confirm data residency, ISO certifications, and access controls. Run a plant-level pilot to validate usability on the floor.
| Category | Metric | Example calc |
|---|---|---|
| Quality | Scrap reduction | 1% scrap drop × annual production value |
| Compliance | Audit time saved | 80 hours saved × loaded hourly rate |
| Admin | Manual updates removed | 10 hrs/week × # of sites |
| Ramp-up | Time-to-competence | Weeks saved × cost per role |
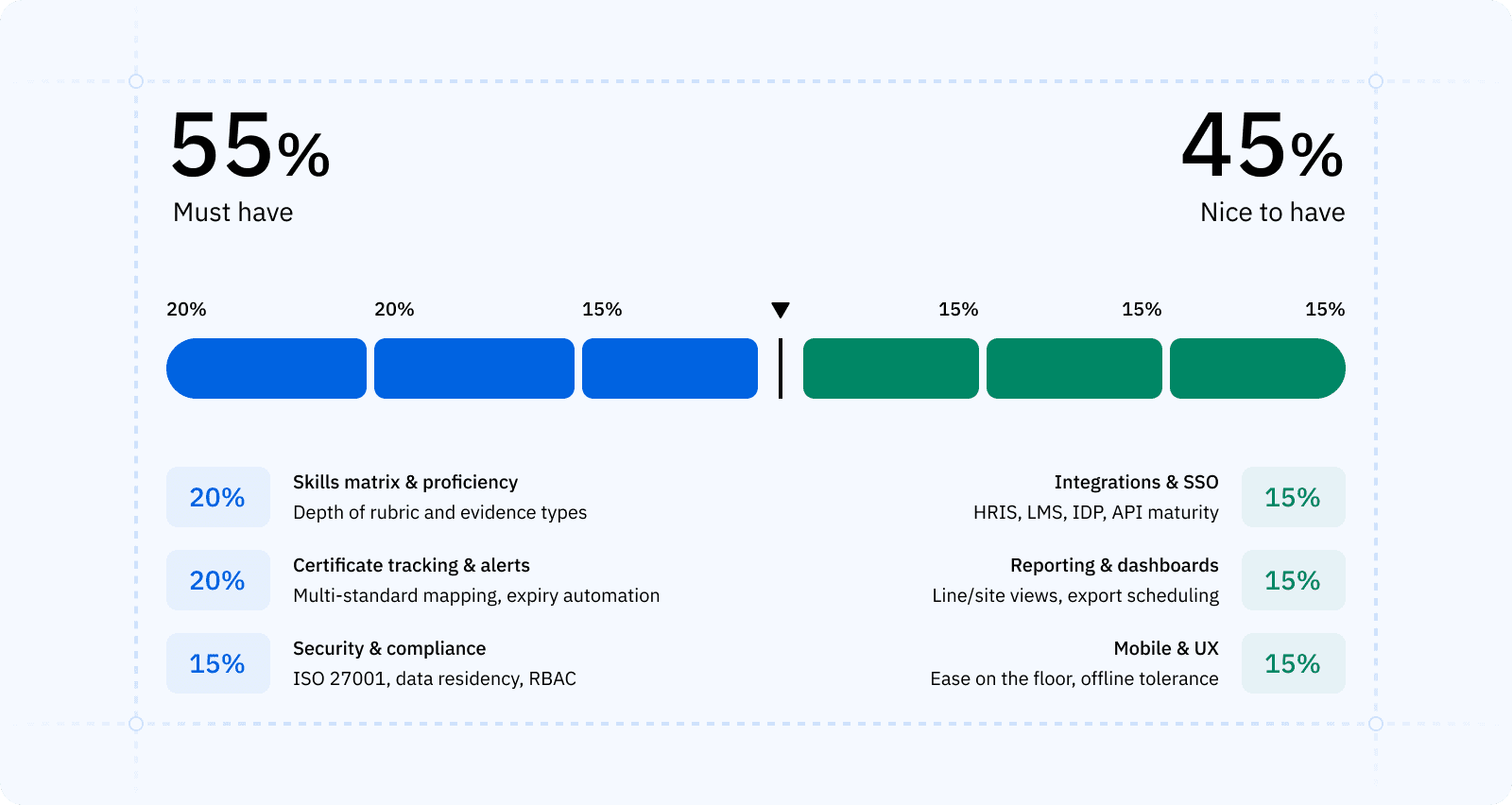
Selection scorecard
| Factor | Weight | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Skills matrix & proficiency | 20% | Depth of rubric and evidence types |
| Certificate tracking & alerts | 20% | Multi-standard mapping, expiry automation |
| Integrations & SSO | 15% | HRIS, LMS, IDP, API maturity |
| Reporting & dashboards | 15% | Line/site views, export scheduling |
| Mobile & UX | 15% | Ease on the floor, offline tolerance |
| Security & compliance | 15% | ISO 27001, data residency, RBAC |
FAQs Copied
-
What is the difference between competence and skill?
-
How often should we reassess proficiency levels?
-
Can we keep using spreadsheets?
-
How do we involve unions and frontline teams?
-
How does it fit with our LMS and HRIS?
-
What KPIs should we track?
-
How long does a pilot take?
-
How do we handle multi-site consistency?
Author Copied
Revisions Copied
Written by: Rick van Echtelt
Copy edited by: Adam Kohut